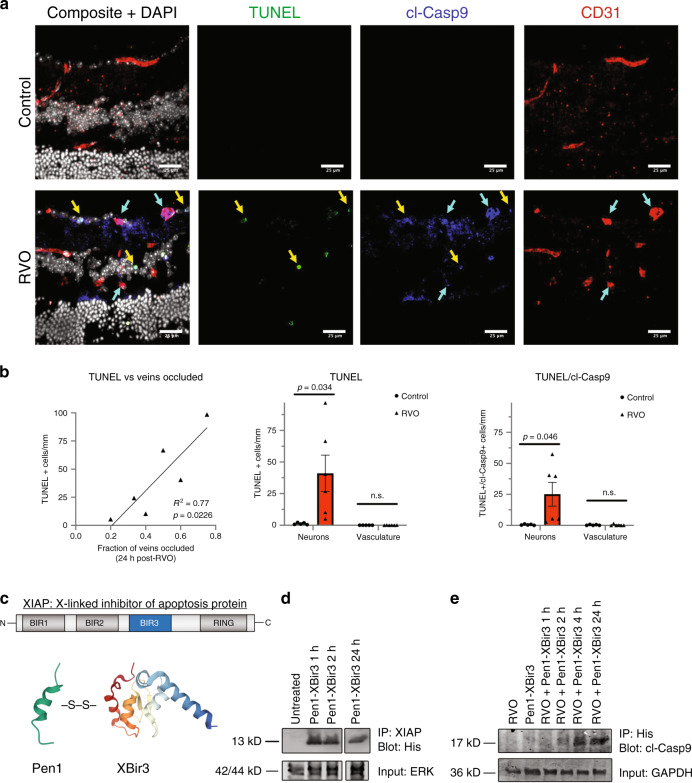
Fig. 3. RVO-induced activation of caspase-9 in endothelial cells is nonapoptotic.
a Retinal cross-sections of Pen1-treated control eyes (n = 5) and Pen1-treated eyes 24 h post-RVO (n = 6) stained for TUNEL (green), cl-caspase-9 (blue), isolectin (red), and DAPI (white). Yellow arrows indicate neuronal cells that are positive for TUNEL and cl-caspase-9. Teal arrows indicate vessels that are positive for cl-caspase-9. b Quantification of (a): induction of TUNEL is correlated with the fraction of veins occluded 24 h post-RVO (linear regression), RVO induces increased expression of TUNEL, and increased coexpression of TUNEL/cl-caspase-9 in neuronal nuclei and not in endothelial cells (vasculature); two-tailed Welch’s t test; mean ± SEM. c The Bir3 domain of XIAP (X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein) is a highly selective endogenous inhibitor of cl-caspase-9. Pen1-XBir3 is generated by crosslinking XBir3 with Penetratin-1, a cell-penetrating peptide. XBir3 and Penetratin-1 structure rendered with Mol*70. d Western blot showing detection of XBir3 in uninjured retinal lysates at 1, 2, and 24 h following administration of Pen1-XBir3 eye-drops in mice. n = 3. e Western blot of target engagement; mice received Pen1-XBir3 eye-drops immediately following induction of RVO. Immunoprecipitation of XBir3 from retinal lysates shows XBir3 binding to cl-caspase-9. n = 2. cl-casp9, cl-caspase-9. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.