Figure 3.
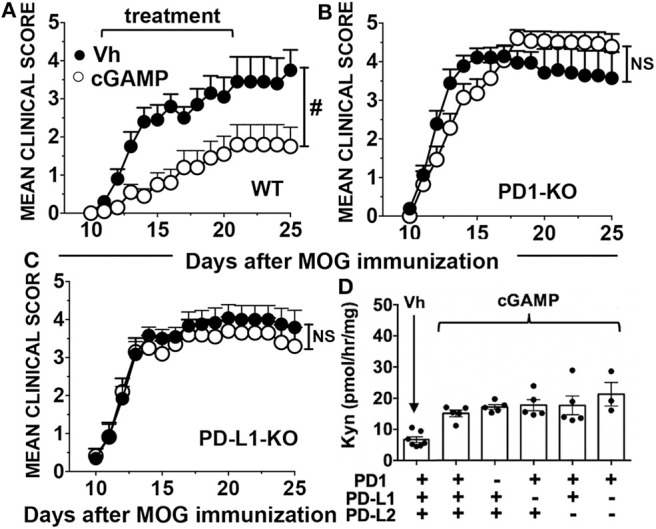
The PD-1/PD-L pathway is required for therapeutic responses to cGAMP. (A–C) EAE was induced in B6 (WT), PD-1-KO, and PD-L1-KO mice, and disease onset and progression was monitored and scored. At EAE onset (day 11) mice were treated with cGAMP every other day until day 21 and control mice were treated with vehicle (Vh; saline). Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA (NS, not significant; #p < 0.0001) and are representative of 2 experiments with n = 6–18. (D) Mice were treated with cGAMP or Vh (saline) and 24 h later spleens were harvested and IDO activity in homogenized tissues was measured by assessing Kyn production ex vivo. Data were analyzed using Student's t-test and Kyn levels were significantly higher in all mice (n = 4–9) treated with cGAMP, B6 (WT, p < 0.001), PD-1-KO (p < 0.0001), PD-L1-KO (p < 0.01), PD-L2-KO (p < 0.05) and PD-L1+L2-KO (p < 0.05) mice relative to basal Kyn levels in vehicle-treated WT mice.
