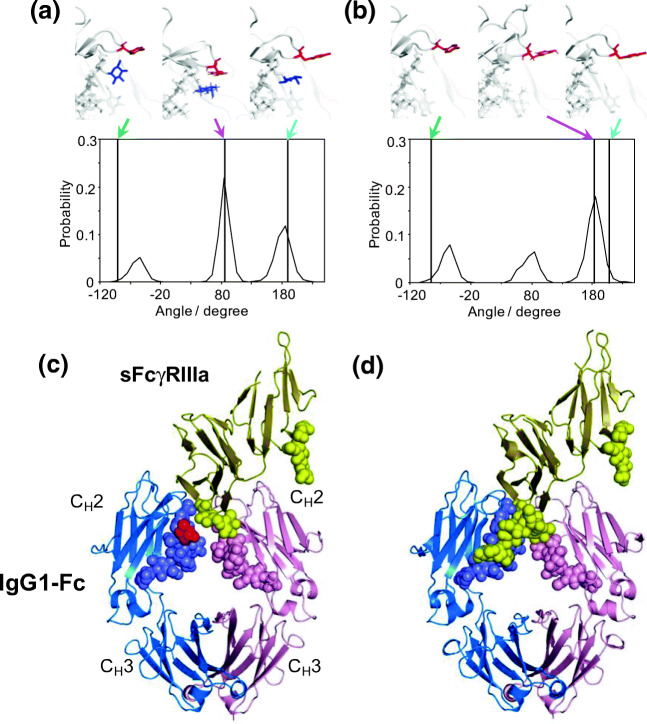
Fig. 3.
Effects of core fucosylation of the Fc N-glycans on conformational dynamics of Tyr296 of IgG1-Fc and the N162 glycan of FcγR. Distributions of χ1 dihedral angles of Tyr296 in the ensemble models derived from MD simulations are plotted for (a) fucosylated IgG1-Fc and (b) nonfucosylated IgG1-Fc. The typical conformational snapshots of derived from the major conformational states (magenta arrows) in the simulation trajectory are shown along with the crystal structures used for building the starting models (green arrows; A, 3AVE; B, 2DTS) and those of sFcγRIIIa-bound Fc (cyan arrows; A, 5XJE; B, 3AY4). Crystal structures of (c) fucosylated and (d) nonfucosylated Fc complexed with bis-glycosylated soluble form of FcγRIIIa (sFcγRIIIa). Chains A and B of Fc are blue and pink, respectively; sFcγRIIIa is yellow. Carbohydrates are represented as spheres. Fuc is colored in red. In the complex of fucosylated Fc, the N162 glycans of sFcγRIIIa gave electron densities only for the reducing-terminal residues, in marked contrast to the observation of the same sFcγRIIIa in complex with nonfucosylated Fc, in which the N162 glycan is extensively involved in interactions with the Fc glycan. Adapted from reference (Yanaka et al. 2019a) and (Sakae et al. 2017) with the modification