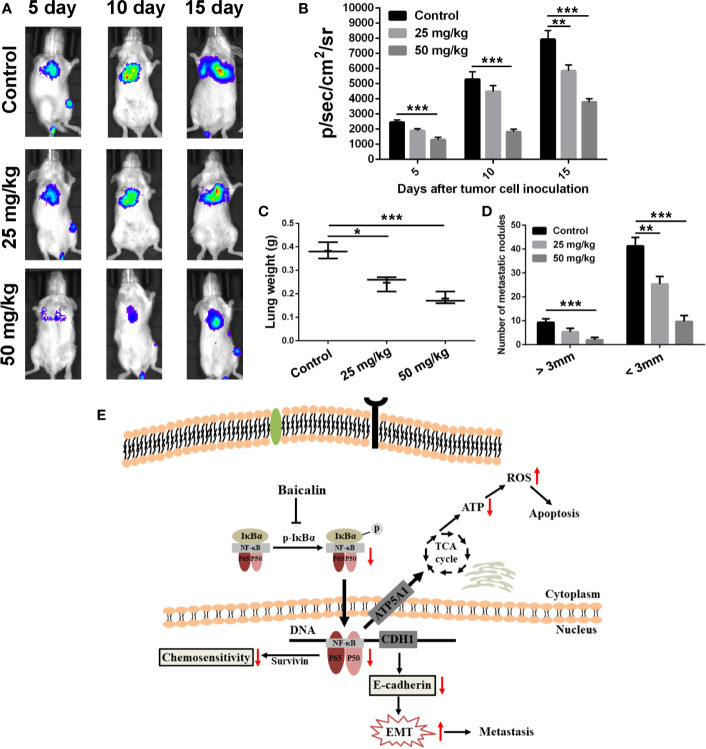
Figure 6.
BA inhibited pulmonary metastasis of breast cancer cells. Female Balb/c mice were intravenously injected with 5 × 105 4T1-Luciferase cells suspended in 100 μl of culture medium containing no FBS or antibiotics to establish pulmonary metastasis tumor mouse model. Five days after inoculation, the mice were intraperitoneally injected with vehicle, 25 mg/kg, or 50 mg/kg of BA every 2 days. (A) Bioluminescent images of mice of different treated groups at determined times. (B) Statistical analysis of bioluminescent signals of mice of different treated groups at determined times. (C) Lungs weight of mice in different treated groups at the termination of animal experiment. (D) Numbers of metastatic nodules (>3 mm and <3 mm) in lung tissues were counted at the termination of animal experiment. (E) Overview of pathways for baicalin-mediated anti-tumor effects on breast cancer cells. Baicalin induced apoptosis, inhibited metastasis, and enhanced chemosensitivity by NF-κB signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. Significant differences are indicated as follows: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.