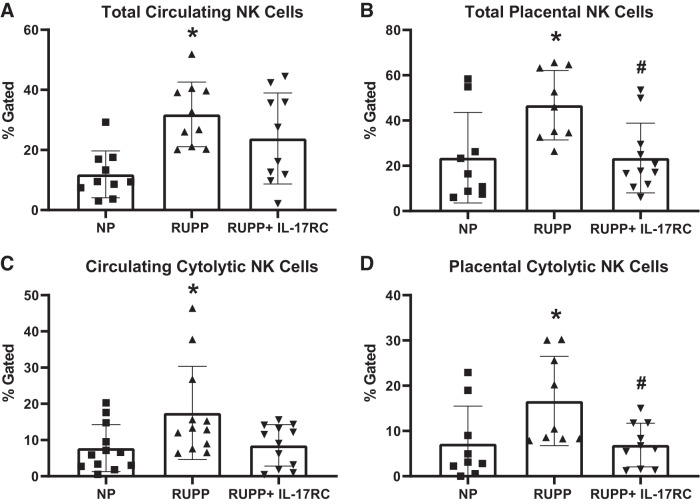
Fig. 3.
Chronic inhibition of IL-17 in reduced uterine perfusion pressure (RUPP) rats results in reduced natural killer (NK) cell activation. A subset of pregnant rats undergoing the RUPP procedure also received a miniosmotic pump infusing 100 pg/day of a soluble IL-17 receptor (IL-17RC) into the intraperitoneal cavity from gestational days (GD) 14–19. On GD19, blood and placentas were collected, processed, and analyzed via flow cytometry to obtain percentages of circulating total (A) and placental total (B) NK cells as well as circulating (C) and placental (D) cytolytic NK cells. Normal pregnant (NP): n = 9–12 rats RUPP: n = 9–12 rats; RUPP + IL-17RC: n = 10–12 rats. All data are expressed as means ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons followed by Tukey’s post hoc correction. *P < 0.05 vs. NP; #P < 0.05 vs. RUPP.