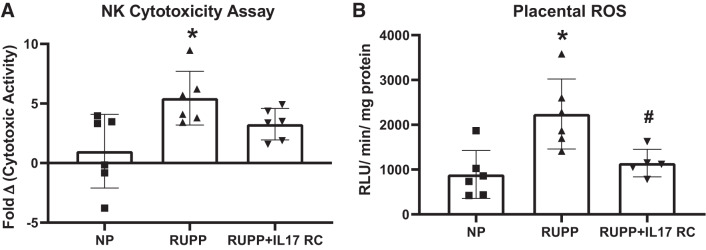
Fig. 4.
Chronic inhibition of IL-17 in reduced uterine perfusion pressure (RUPP) rats blunts natural killer (NK) cytotoxicity and normalizes placental oxidative stress. A subset of pregnant rats undergoing the RUPP procedure also received a miniosmotic pump infusing 100 pg/day of a soluble IL-17 receptor (IL-17RC) into the intraperitoneal cavity from gestational days (GD) 14–19. A: the cytotoxic activity of isolated placental NK cells was measured using a cytotoxicity assay based on lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release. The results are expressed as fold change in cytotoxic activity. B: superoxide production from placental homogenates was analyzed using the lucigenin assay. ROS, reactive oxygen species. The results are expressed as relative light units (RLUs)·min−1·mg−1. Normal pregnant (NP): n = 6 rats; RUPP: n = 6 rats; RUPP + IL-17RC: n = 5–6 rats. All data are expressed as means ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons followed by Tukey’s post hoc correction. *P < 0.05 vs. NP; #P < 0.05 vs. RUPP.