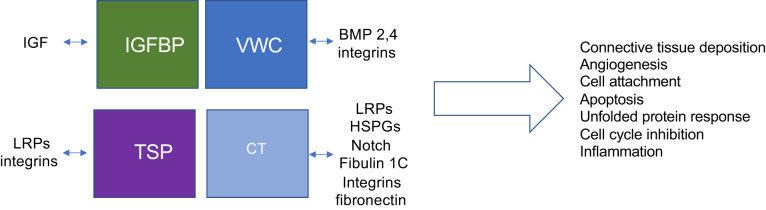
Fig. 1.
Combinatorial interactions dictate cellular communication network (CCN) function. Each domain of CCN proteins interacts with different ligands. What CCN domains are present in the microenvironment depends on which CCN molecules are being synthesized [for example, CCN5 lacks the heparin-binding carboxy-terminal (CT) domain], protease activity, and differential splicing. The affinity of CCN molecules for each ligand is likely to vary. Thus, the overall biological effect of CCN proteins can vary widely depending on bioavailability of CCN proteins, their modules/fragments, and their interacting partners. CCN proteins act as central mediators of mechanotransduction. BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; HSPG, heparan sulfate proteoglycans; LRP, lipoprotein receptor-related protein; TSP, thrombospondin-1; VWC, von Willebrand factor C.