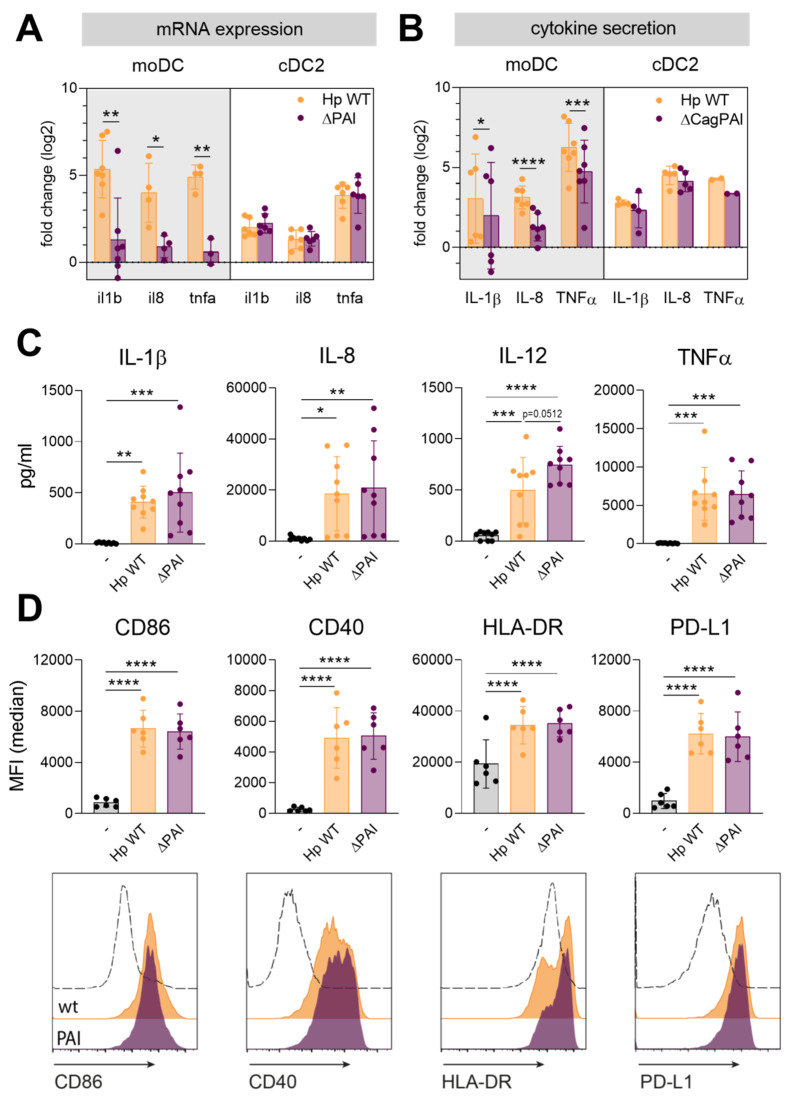
Figure 1.
Activation of CD1c+ conventional DC (cDC2s) is similar upon infection with Helicobacter pylori wt or a mutant lacking the T4SS. (A,B) Monocyte-derived DCs (moDCs) or cDC2s were infected with H. pylori wt or a mutant lacking the type IV secretion system (ΔPAI) at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 5. One hour post-infection, mRNA expression was analyzed by qPCR (A). After 4 h, cytokine secretion was evaluated by ELISA or multiplex technology (B). Log2 fold changes compared to the untreated sample are shown. For comparing fold changes of Hp wt and PAI-infected samples, a paired t-test was performed. (C) Cytokine and chemokine secretion by cDC2s was measured by multiplex technology 16 h post-infection. (D) Surface marker expression was monitored by flow cytometry. Median fluorescence intensity of six donors (upper panel) and histograms of one representative donor (lower panel) are shown. Dots represent individual donors, bars show means ± SDs. For statistical analysis, repeated-measures, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test was performed. (* p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001).