Figure 2.
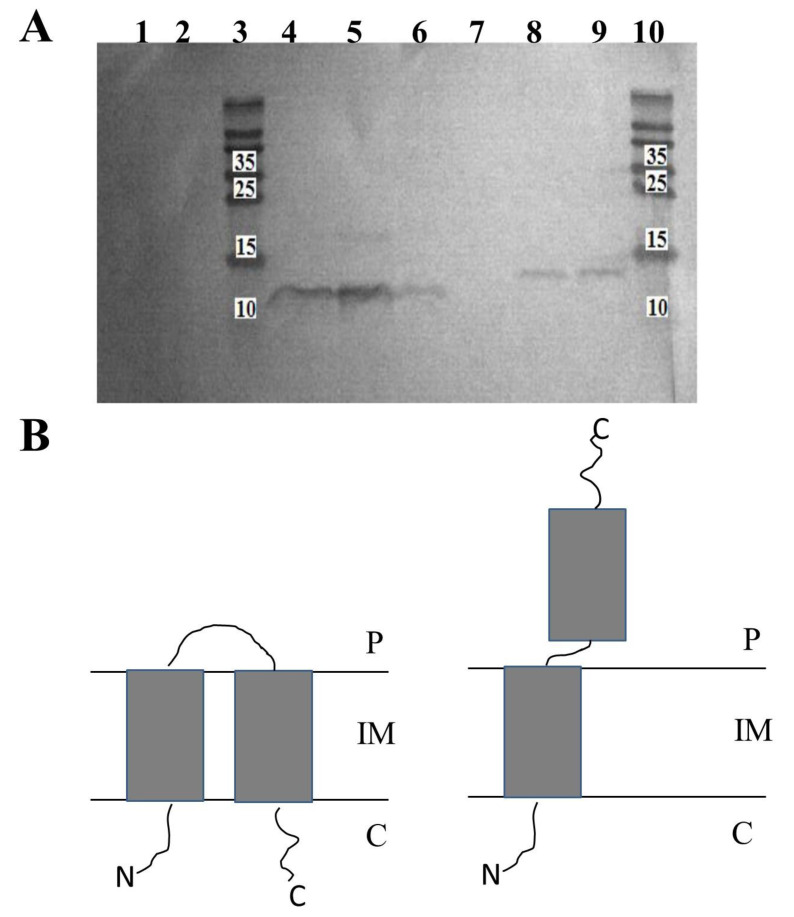
Topology of HP1 holin in the inner membrane of E. coli (A) Western blot analysis of membrane-embedded proteins isolated from inverted membrane vesicles (IMV) prepared from E. coli BL21(DE3) expressing His-tagged holin protein from HP1 phage. When indicated, the peptidyl termini present outside IMV were removed by proteinase K treatment before the extraction of the membrane-embedded protein. Membrane proteins extracted from E. coli BL21(DE3) cells carrying control pCHisHol without induction with IPTG (line 1) or control pNHisHol without induction with IPTG (line 2); Membrane proteins extracted from E. coli BL21(DE3) cells carrying pCHisHol extracted from: (line 4) IMV treated with proteinase K, (line 5) IMV without the proteinase K treatment, (line 6) whole cells without proteinase K treatment. Membrane proteins extracted from E. coli BL21(DE3) cells carrying pNHisHol extracted from: (line 7) IMV treated with proteinase K, (line 8) IMV without the proteinase K treatment, (line 9) whole cells without proteinase K treatment. Lines 3 and 10: Protein Ladder PageRulerTM (ThermoFisher). Numbers represent molecular weight of ladder proteins in Kda (B) Schematic model of HP1 holin (P: periplasm, C: cytoplasm, IM: inner membrane). Up: the inactive, non-lethal form, down: the active-lethal form (experimentally confirmed). The exact activation mechanism of holin from non-lethal to lethal form is unknown.