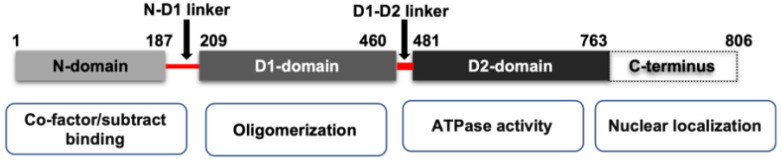
Figure 1.
The scheme of the mammalian isoform of VCP domains and their function. VCP is constituted by one binding domain N-domain, two ATPase domains (D1 domain and D2 domain) and a C-terminus. N-domains are responsible for substrate recognition and binding. The D2 domain contributes to the major ATPase activity of VCP, while the D1 domain is responsible for the assembly of VCP homohexamer. The N-domain and D1 domain are connected by an N-D1 linker, and the D1 and D2 domains are connected by D1–D2 linker.