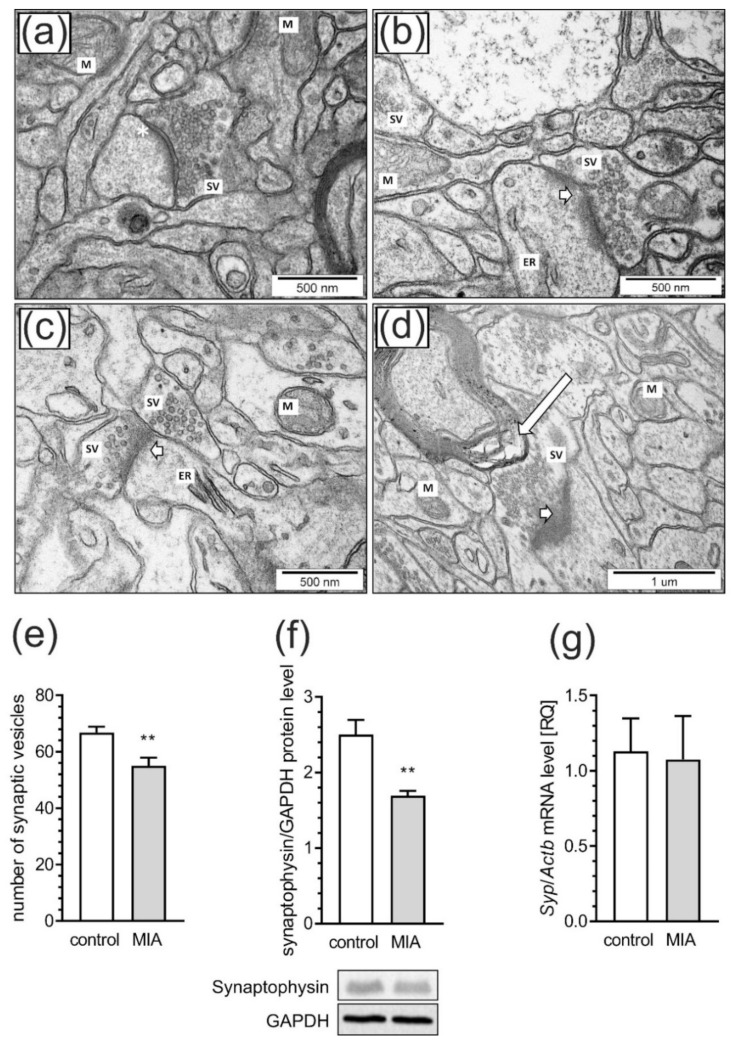
Figure 9.
MIA evokes synaptic alteration in rat brain cortex. The effects of prenatal LPS exposure on ultrastructural changes of synapses in male offspring at PND 52 were examined in the somatosensory cortex by transmission electron microscopy. Representative pictures were presented (Figure a–d). In the control group (a), normal structure of neurons, neuropil, well-defined structure of synapses with accurate post-synaptic density (asterisks), distribution of synaptic vesicles (SV), and well preserved mitochondria (M) were observed. In the MIA group (b–d), observations include features of neurons and neuropil swelling, reduced packing density of SV in the presynaptic area, blurred structure of synaptic cleft without clearly marked pre- and postsynaptic membranes (short arrows on Figure b–d). Moreover, disturbed synaptic membrane, ultrastructural changes in mitochondria with blurred cristae structure (M on Figure b,c), changes in myelin structure (long arrow on Figure d) and swollen endoplasmic reticulum (ER on Figure b) were present. (e) Quantitative analysis of synaptic vesicle numbers. (f) Densitometric analysis of synaptophysin normalized to GAPDH immunoreactivity with representative Western blot. (g) Gene expression of Syp as measured by real-time PCR and normalized to Actb (β-actin). Data represented the mean value ± S.E.M. (e–n = 4, f–n = 6–9, g–n = 3–4) for ultrastructural analysis and n = 6 for gene expression and protein levels. Data were analyzed using Student’s t-test. ** p < 0.01 compared to control group.