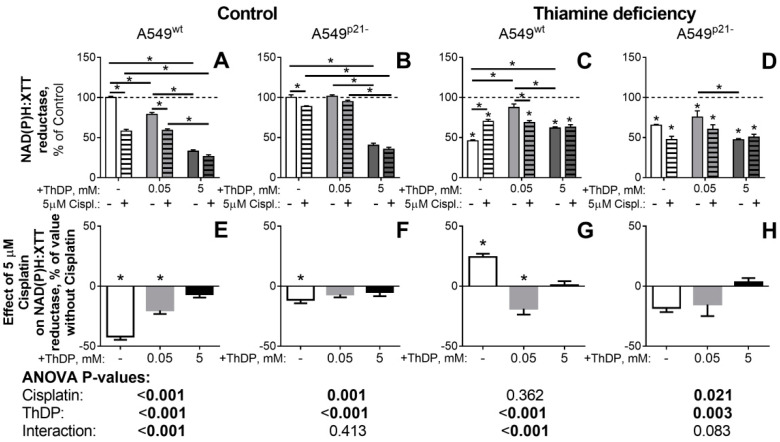
Figure 5.
Influence of cisplatin (Cispl.) on p21-dependent responses of NAD(P)H:XTT reductase activity of A549 cells to variation in the thiamine/ThDP levels. A549wt (A,C, E,G) or A549p21- (B,D,F,H) cells were cultured in DMEM prepared with 4 mg/L thiamine hydrochloride (Control, A, B, E, F) or without thiamine (Thiamine deficiency, C, D, G, H). 24 h after supplementation with indicated concentrations of ThDP (shades of grey) and/or cisplatin (5 μM, hatched columns), NAD(P)H:XTT reductase activity was assayed. Values obtained without ThDP supplementation are presented by white columns, those at 0.05 or 5 mM ThDP—by gray or black columns, correspondingly. In the upper part (A–D), cellular NAD(P)H:XTT reductase activity is normalized to the activity of the control A549wt or A549p21- cells to show combined effects of thiamine/ThDP and cisplatin on cellular viability. In the lower part (E-H), cellular NAD(P)H:XTT reductase activity is normalized to the corresponding value without cisplatin to show the specific effect of cisplatin under each variation in the thiamine/ThDP levels. The data of at least three independent experiments are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistically significant differences (p < 0.05, shown by asterisks) are determined by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Horizontal lines show the groups compared. Asterisks above the bars in C and D indicate the statistically significant differences between the corresponding thiamine deficient cells and cells with standard thiamine level. Asterisks in E–G indicate the statistically significant effects of cisplatin vs the same condition without cisplatin. ANOVA significances of the factors (cisplatin and ThDP) and their interactions are given below the graphs, with significant (p < 0.05) values in bold.