Fig. 3.
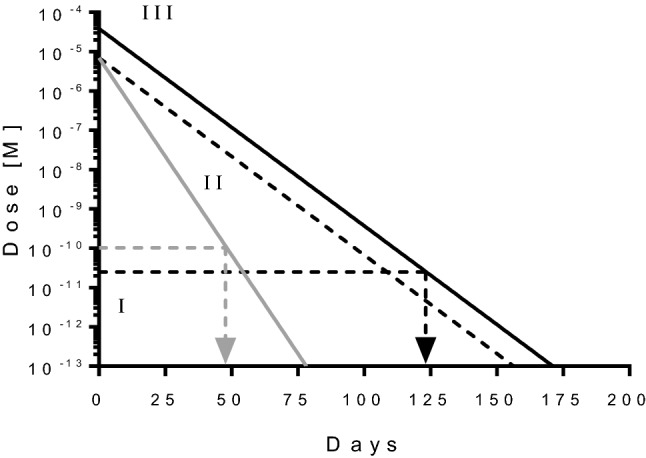
Schematic illustration of duration of action engineering of abicipar. Drug concentration of abicipar (black line) and ranibizumab (gray line) are shown over time. Assuming reference ranibizumab is administered 50 μl/0.5 mg intravitreally, and the drug has a half-life in the 1.5 ml rabbit eye of 3 days and an inhibition constant IC50 of about 100 pM, then the drug would stop being efficacious when reaching a concentration equivalent to the IC50, i.e. duration of action of about 48 days. Three aspects help increase the duration of action of abicipar: (I) improving the potency to lower values in combination with high drug stability ensure that the drug is also active at very low amounts; (II) engineering the half-life as such, requiring high drug stability; (III) applying higher doses. Assuming abicipar exhibits an IC50 of about 25 pM [26], has an ocular half-life of 6 days in the rabbit eye, and that it can be applied at about 5.5 times the molar amounts of ranibizumab, then it would take 124 days (4 months) for the vitreal concentration of abicipar reaches the IC50 concentration of 25 pM
