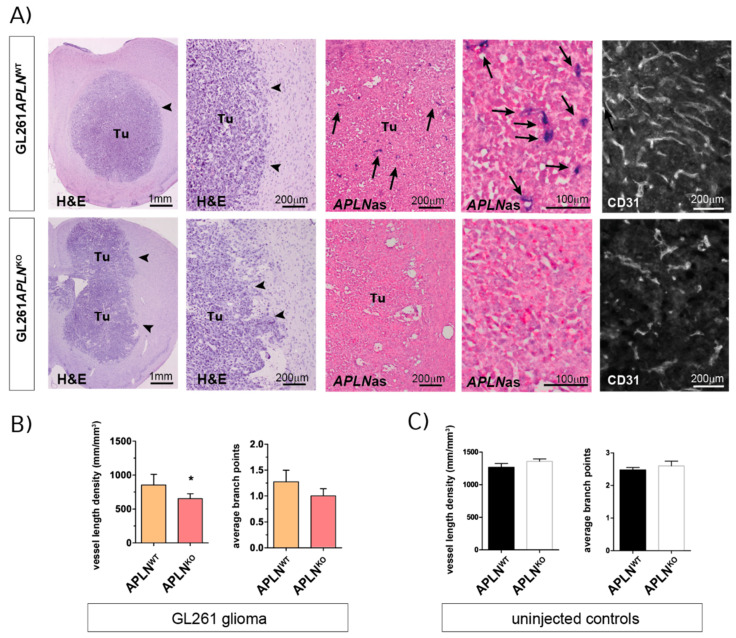
Figure 2.
Endothelial APLN expression controls formation of a complex GBM vasculature. Orthotopic GL261 implants in APLNWT or APLNKO mice 21 days post-implantation (dpi). (A) The panels on the left indicate the tumor (tumor boarder highlighted by arrowheads) in the right brain hemisphere in overview and close up view on Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E) sections. The in situ hybridization panels in the middle show the loss-of vascular APLN expression (arrows) in the tumor in overview and close up view when comparing APLNWT to APLNKO mice. The CD31-immunostaining shown in the panel on the right illustrates the reduced vessel density in APLNKO mice. (B) Vessel length density (VLD) was assessed on CD31 immunofluorescent brain slides and demonstrated a significant decrease in APLNKO mice. In addition, vascular complexity measured by the average branch points (ABP) was reduced in APLNKO as compared to APLNWT. (C) In the healthy brain, VLD and ABP do not differ in APLNKO compared to APLNWT mice. Data of n = 9 APLNWT vs. 6 APLNKO mice are reported as mean +/-SEM; statistical significance (students test) is indicated * p < 0.05.