Figure 3.
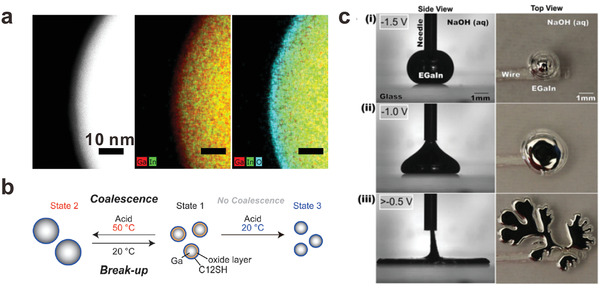
Attributes of liquid metal particles. a) TEM images of a liquid metal nanoparticle. The core is liquid EGaIn, but the solid shell (cyan) is ≈3 nm thick layer of gallium oxide. Adapted with permission.[ 62 ] Copyright 2015, Wiley‐VCH. b) The size of liquid metal nanoparticles can be tuned reversibly through modulating the balance between the oxide layer and the stabilization effect of surfactants. Reproduced with permission.[ 70 ] Copyright 2015, Wiley‐VCH. c) Without the oxide, the surface energy of liquid metal particles is large, yet can be lowered by applying a modest voltage that drives electrochemical oxidation of the surface. The applied voltage can lower the tension to the point that “fingers” form. Note: the open circuit potential is −1.5 V, and thus a potential of −1.5 V implies zero external voltage. Reproduced with permission.[ 53 ] Copyright 2014, National Academy of Sciences.
