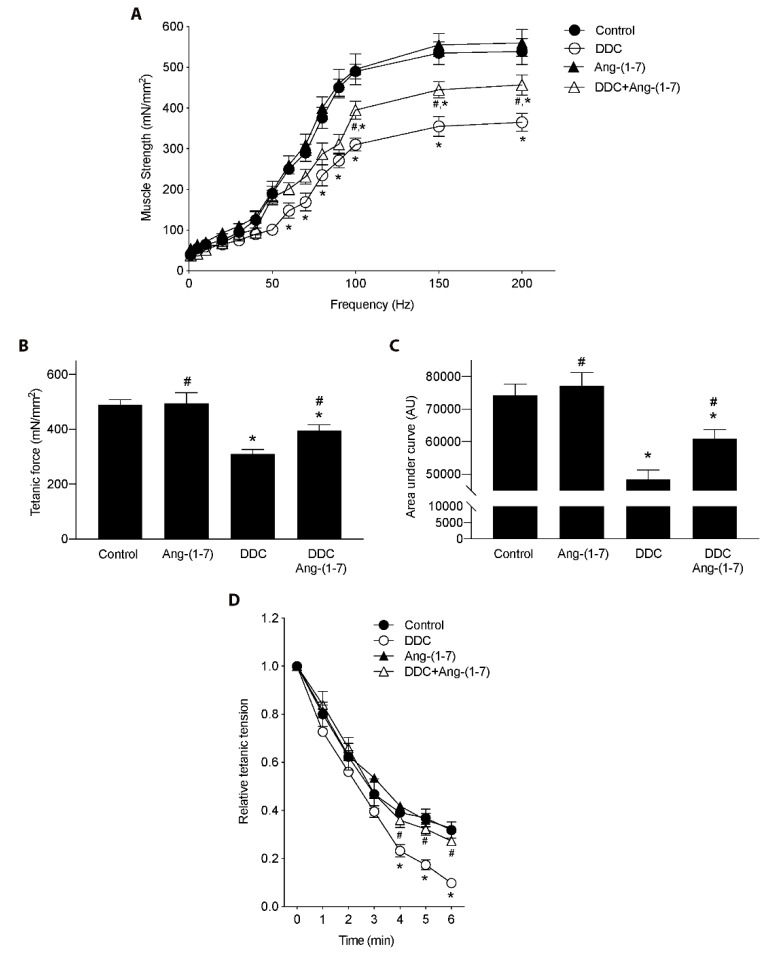
Figure 2.
Preventive effect of Ang-(1-7) on the decrease of muscle strength and fatigue induced by DDC diet in gastrocnemius muscle of mice. Male mice C57BL/6J (16 weeks old) were randomly separated into four groups: Control, Ang-(1-7), DDC, and DDC + Ang-(1-7). DDC was administrated by diet for six weeks, whereas Ang-(1-7) was administered through osmotic minipumps for six weeks. Five or six animals per group were used for three independent experiments. At the end of the experiment, gastrocnemius muscle was excised, and electrophysiological assays were performed. (A) Muscle strength was measured at different frequencies and represented as mN/mm2. (* p < 0.05 vs. Control; # p < vs. DDC. Two-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). (B) Maximal tetanic force in mN/mm2. (* p < 0.05 vs. Control; # p < vs. DDC. One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (C) Muscle strength represented as area under each curve of experiments showed in A. (* p < 0.05 vs. Control; # p < vs. DDC. One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (D) Fatigue was evaluated as tension relative to tetanic tension for six min. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. (* p < 0.05 vs. Control; # p < vs. DDC. Two-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test).