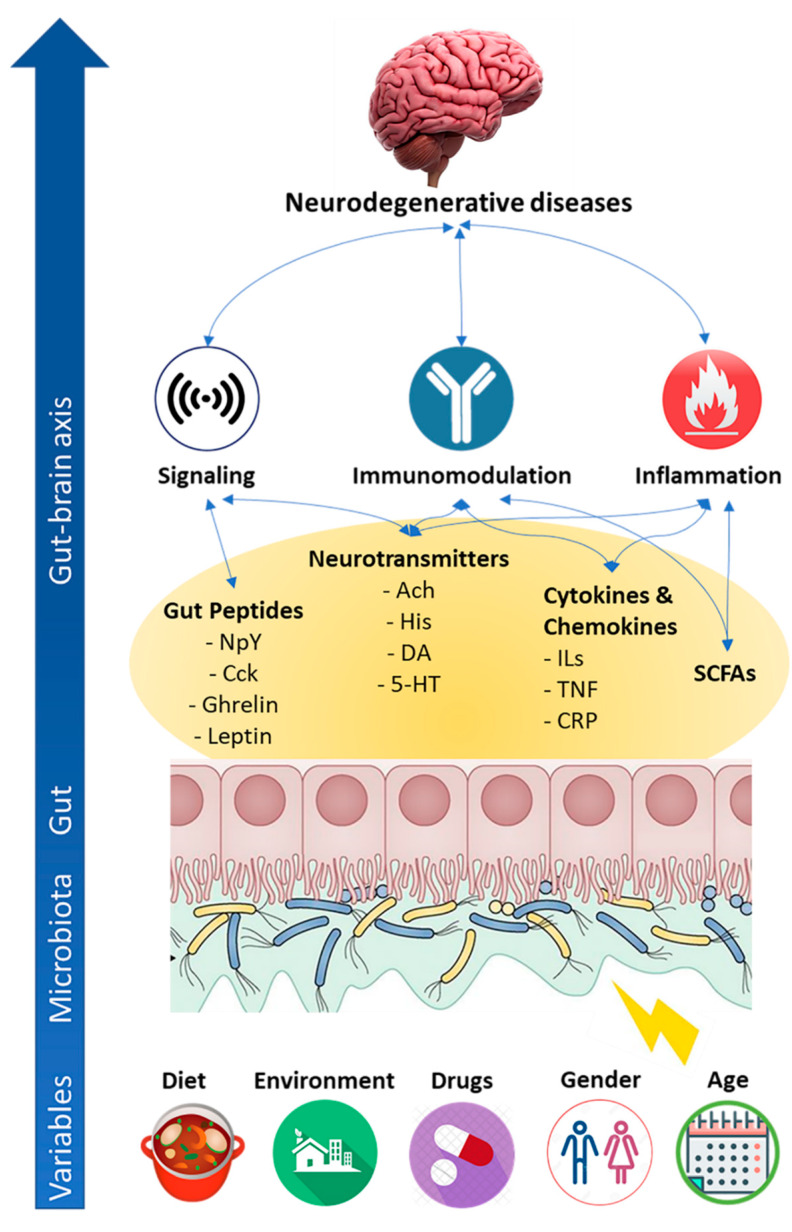
Figure 1.
Major mechanisms employed by gut microbiota to impact neurodegenerative diseases. The figure depicts the most relevant endogenous (i.e., age, gender) and environmental (i.e., diet, environment, and drugs) variables affecting gut microbiota composition and functions. In turn, microbiota dysbiosis impacts neurodegenerative diseases through direct production of neuroactive molecules (e.g., short-chain fatty acid (SCFAs), neurotransmitters) and/or stimulation of neuroactive mediator production by the secretory epithelial cell (e.g., Citokynes, chemokine, gut peptides). Examples of neuroactive molecules are mentioned in the figure. Ach: Acetylcholine; His: Histidine; DA: Dopamine; 5-HT: Serotonin; NpY: Neuropeptide-Y; CcK: Cholecystokinin; ILs: Interleukins; TNF: Tumor Necrosis Factor; CRP: C-Reactive Protein.