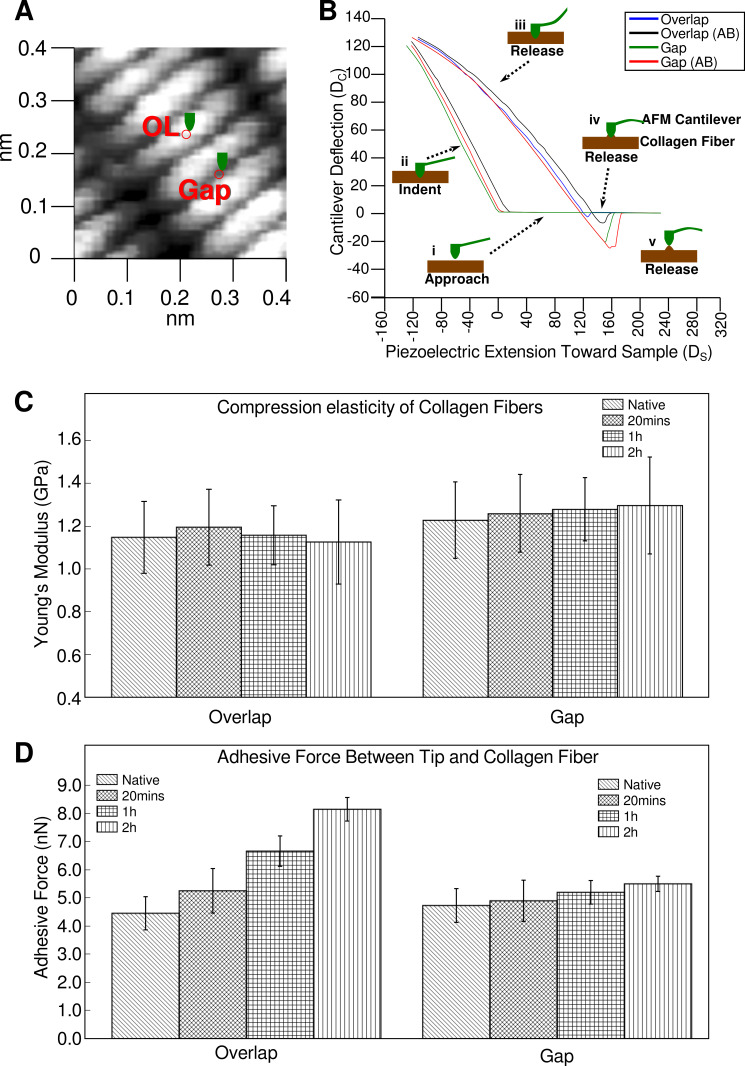
Figure 1.
Elasticity and adhesive behavior of collagen fiber determined by atomic force microscopy (AFM) nanoindentation. (A) The region of interest with gap and overlap (OL) were marked where nanoindentation was performed; (B) Typical force-distance curves of collagen fibers recorded at overlap and gap zones in native and treated states, respectively, with a ~20 nm indentation. The plot is also annotated with the process of indentation (i–v) from the AFM tip approaching the sample through to indenting and releasing after adhesion. Data from the force curves are used to calculate transverse elasticity and adhesion force; (C) Transverse elasticity coefficient and Young’s modulus (KS, and ES) of native and antibody treated collagen fibers at overlap and gap zones in drying process; (D) Adhesion force (FA) between AFM tips and collagen fiber at overlap and gap zones with time of antibody incubation prior to data collection. Note the significant increase in adhesive force for the overlap zone of the sample treated with gold-conjugated antibody.