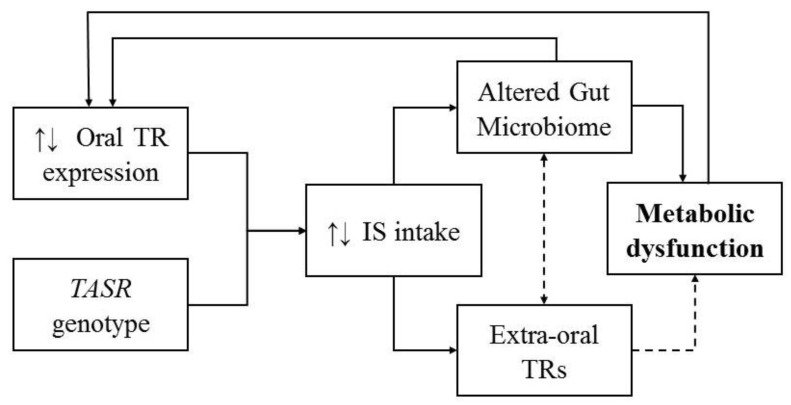
Figure 1.
Potential interactions between taste receptors (TR), intense sweeteners (IS), the gut microbiome and metabolic conditions. Oral taste receptor expression levels, along with TASR genotypes, determine the palatability or aversiveness of sweeteners, which affects IS intake levels. IS may then activate gastrointestinal T1Rs and T2Rs, which may lead to altered metabolic hormone secretion. Some IS also have an effect on the composition and function of the intestinal microbiome, which may also lead to metabolic alterations. Interestingly, both an altered gut microbiome and certain metabolic disturbances may alter oral taste receptor expression levels. Finally, it is hypothesised that extra-oral taste receptor expression may be altered in response to intestinal dysbiosis, and this may impact the expression of extra-oral taste receptors, resulting in metabolic alterations.