Figure 1.
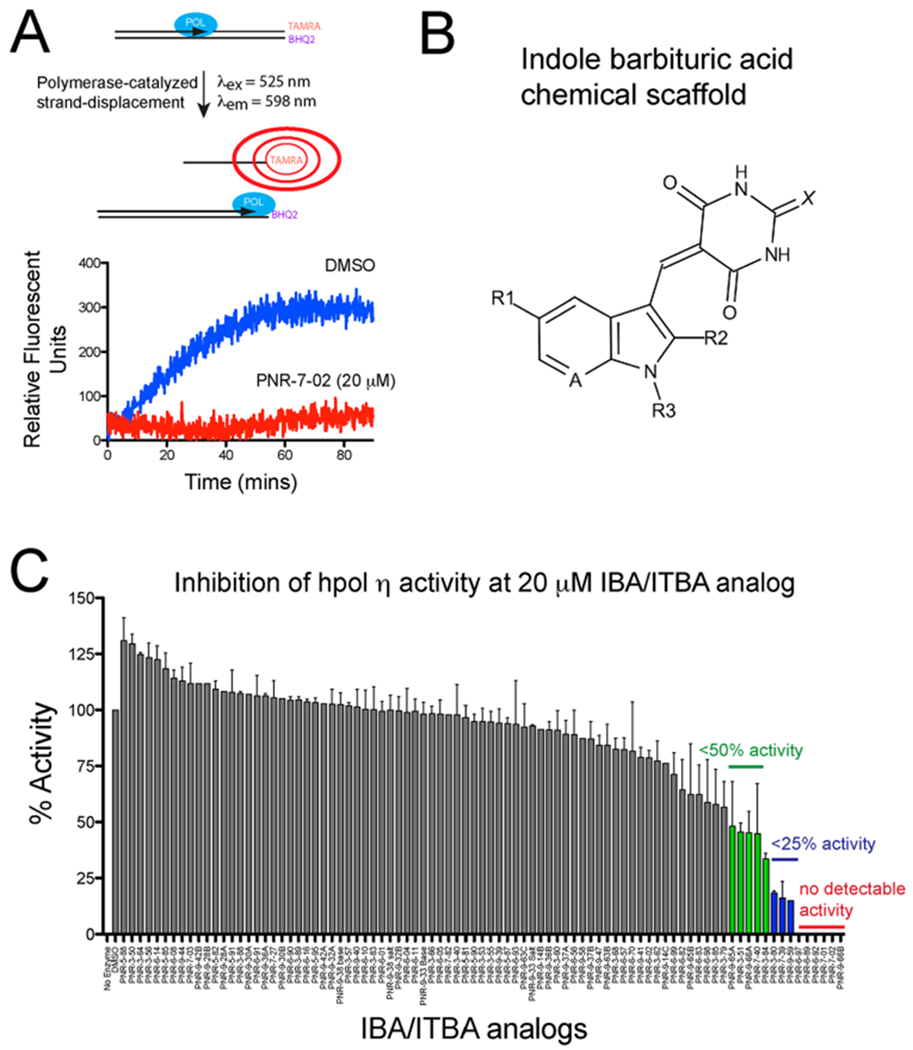
Structure–function studies identified PNR-7-02 as an inhibitor of hpol η with improved potency relative to other indole-derived compounds. (A) Schematic illustration of the pol activity assay. (B) General chemical structure of the parent indole barbituric acid (IBA) scaffold that incorporates all analogues tested for inhibition of TLS pol action. The availability of multiple sites of modification (R1–R3, A, and X positions are noted on the parent scaffold) allowed a useful structure–activity study to be performed. (C) Catalytic activity of hpol η (2.5 nM) was measured in the presence of 85 IBA and indole thiobarbituric acid (ITBA) derivatives (20 μM) to identify structure–activity relationships important for inhibition of this TLS pol. The results represent the mean (±SD) for experiments performed in triplicate. See Supporting Information Table S1 for the chemical structure and details regarding pol activity for each compound.
