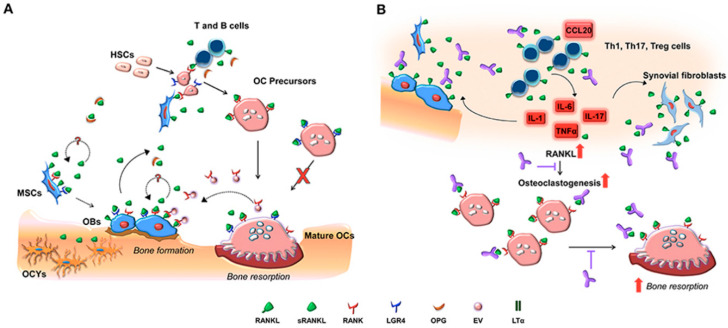
Figure 2.
Diagrammatic illustration of molecular and cellular players taking part in RANK, RANKL, and OPG signaling in bone during physiological (A,B) pathological conditions. Soluble RANKL synthesized by osteoblasts and immune cells induce osteoclastogenensis when attaching to RANK on osteoclast precursors [35]. OPG is the soluble decoy receptor for RANKL. The expression of RANK by mesenchymal stem cells and osteoblasts points to a potential RANKL autoregulatory mechanism affecting bone deposition. Furthermore, extracellular vesicles (EV) initiate a reverse signaling on osteoblast (B), depicting enhanced synthesis of RANKL by immune cells and osteoblastic cells [35]. This exaggerates osteoclast generation and bone loss. Image adapted with kind permission from the publisher.