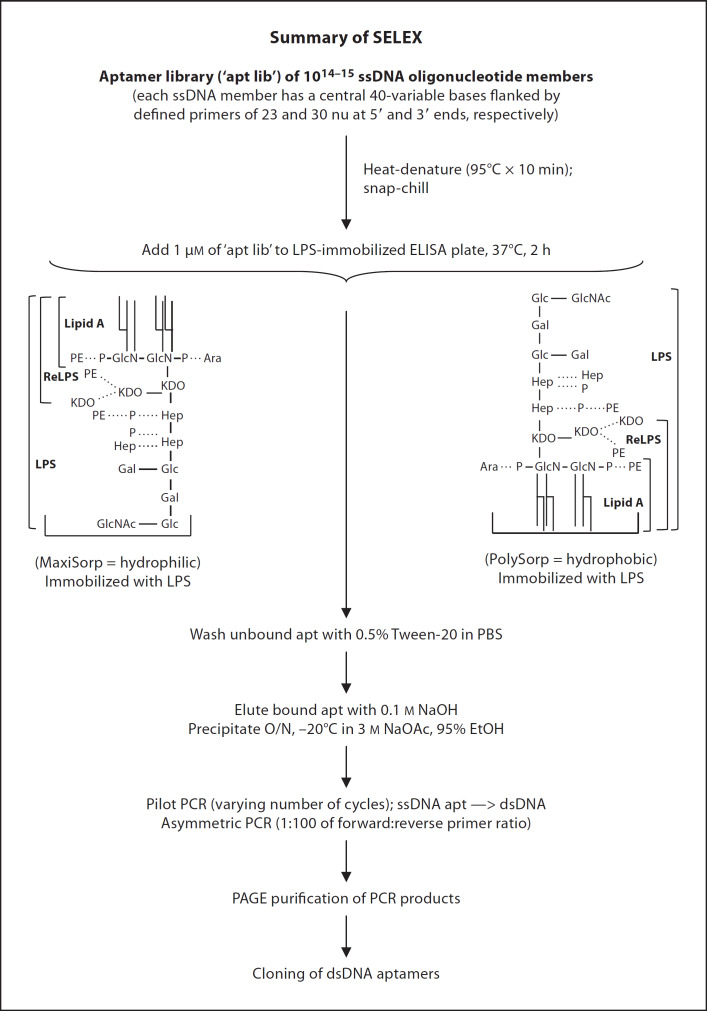
Fig. 1.
Schematic summary of SELEX procedure. The PolySorpTM and MaxiSorpTM 96-well plates (Nunc) were coated with 4 µg/ml (˜1 µM containing 400 EU/ml) of LPS from E. coli. The ssDNA aptamer library (‘apt lib’ containing 1014–15 members) was heat-denatured at 95°C for 10 min and cooled immediately on ice. An aliquot of 1 µM of the ‘apt lib’ was used in the first round of selection. The ssDNAs were incubated with the immobilized LPS at 37°C for 2 h. The non-specifically bound ssDNAs were washed off with PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Bound aptamers were eluted with 100 mM NaOH and precipitated overnight (O/N) at −20°C in 3 M NaOAc and 95% ethanol. The selected ssDNA aptamers were used as templates in pilot PCR with varying number of cycles to produce dsDNA templates with few aberrant products. The random dsDNA was used as template in asymmetric PCR (primer ratio of 1:100 of reverse:forward) at different amplification cycle numbers followed by large-scale asymmetric PCR with the desired cycle number. The PCR products were PAGE-purified. As the aptamers became purer and more specific for the target, the amount of LPS and the incubation period between aptamers and LPS were gradually reduced in progressive rounds to increase the stringency of selection.