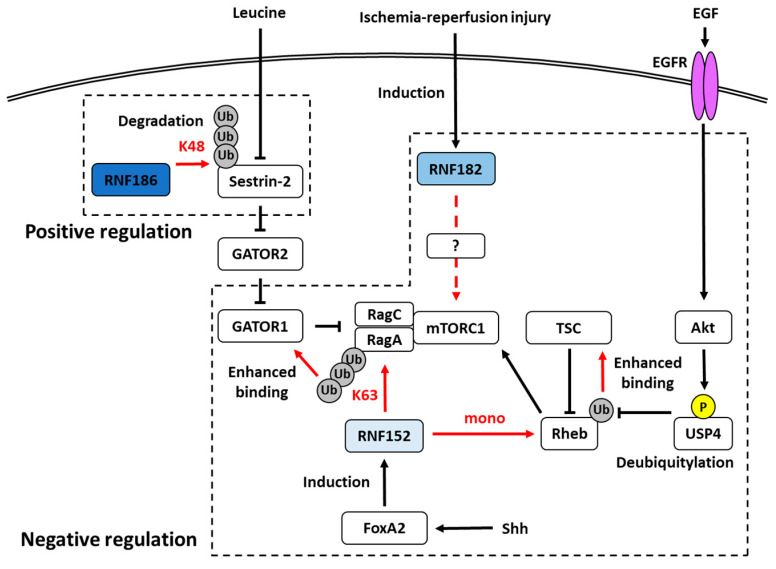
Figure 2.
RNF186, RNF182, and RNF152 are involved in the regulation of the mTORC1 pathway. RNF186 regulates positively by degrading Sestrin-2 ubiquitylated with K48-linked chain, whereas RNF182 and RNF152 are native regulators. RNF152 involves two pathways: the K63-linked ubiquitylation of RagA and the mono ubiquitylation of Rheb. The ubiquitylated RagA and Rheb enhance the binding performance with GATOR1 and TSC, respectively. Phosphorylated USP4, which is identified as a DUB for Rheb, deubiquitylates the ubiquitylated Rheb and cancels the negative regulation by mono ubiquitylation. USP4 is phosphorylated by the EGF-Akt pathway. Shh-dependent FoxA2-transcriptional activity induces RNF152 expression. The expression of RNF182 is induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury; however, the mechanism of mTORC1 suppression by RNF182 remains unknown. The arrows indicate activation, and the T-bars indicate inhibition. The red arrows indicate the effects of ubiquitylation by RNF186 or RNF152. The red characters indicate the types of ubiquitylation by RNF186 or RNF152. The dotted arrow indicates that the detailed mechanism is unknown.