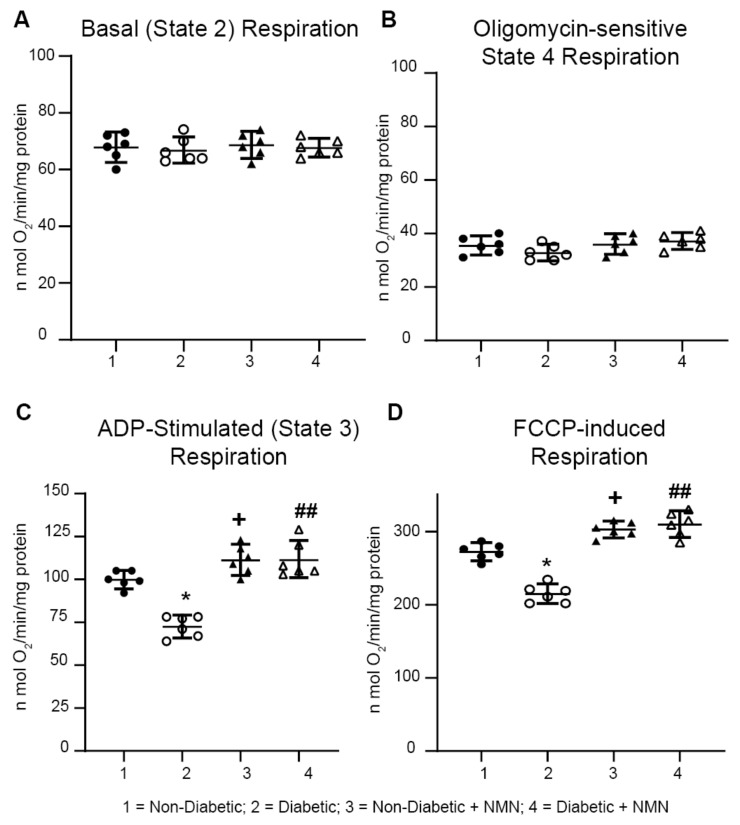
Figure 4.
Impaired mitochondrial respiration in Diabetic rats was prevented by NMN treatment. Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was measured at basal level with the subsequent and sequential addition of ADP, oligomycin, FCCP, and rotenone + antimycin A to hippocampal mitochondria. State 2, State 3, State 4 (oligomycin-sensitive), and FCCP-induced respiration rates were measured. ADP-stimulated and uncoupled respiration was significantly decreased in Diabetic rats compared to Non-Diabetic rats. Administration of NMN significantly increased both ADP-stimulated and uncoupled respiration. Spare respiratory capacity was calculated after subtracting the basal respiration from uncoupled respiration and was significantly higher (p < 0.05) in NMN treated Non-Diabetic and Diabetic hippocampal mitochondria. * p < 0.05 Diabetic vs. Non-Diabetic; + p < 0.05 Non-Diabetic vs. Non-Diabetic + NMN; ## p < 0.01 Diabetic vs. Diabetic + NMN.