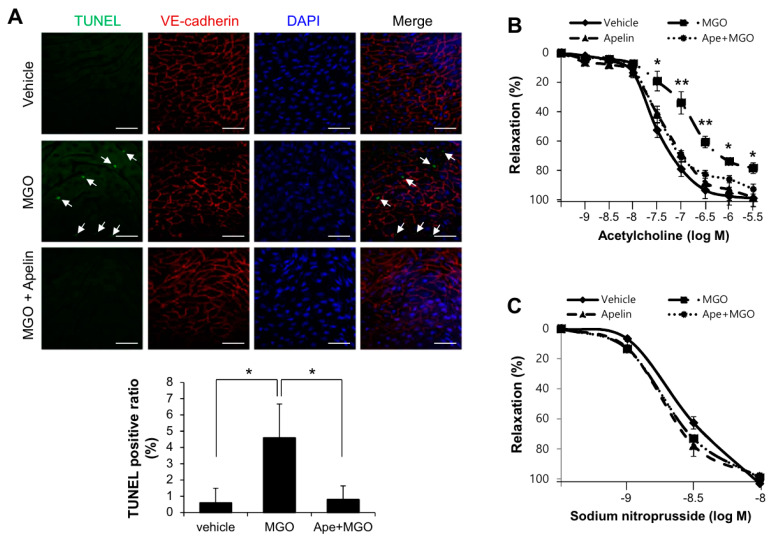
Figure 3.
Apelin-13 protects aortic vessels from MGO-induced endothelial dysfunction. To determine the role of apelin-13 on MGO-induced cell apoptosis and endothelial dysfunction ex vivo, C57BL/6 mice were anesthetized and aorta was isolated. (A) Aorta treated with MGO (100 µM) for 24 h, with or without apelin-13 (1 µM) pretreatment was stained with anti-VE-cadherin antibody for endothelial cell junction. Apoptosis was measured by TUNEL staining using the In Situ Cell Death Detection Kit (Roche, Indianapolis, IN) as described in the Materials and Methods section. Signals were observed under the confocal microscope (×400). Arrows indicate TUNEL positive cells which are apoptotic endothelial cells. Scale bars: 100 µm. Quantification of apoptosis is shown as the percentage of TUNEL positive cells. More than 200 cells were counted for each category. Data represent means ± SDs. * p < 0.05 (n = 5). (B,C) The effect of acetylcholine on phenylephrine-induced vessel contraction in mouse aortic rings. (B) Mouse aortic rings were preincubated with phenylephrine (10−7 M) and then exposed to acetylcholine (10−9–10−6 M). The results shown are representative of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 vs. MGO treated with apelin-13 group (Ape+MGO). (C) Dose-responses to sodium nitroprusside, nitric oxide donor, of phenylephrine-induced precontracted aortic rings. Results are presented as the means ± SDs. n = 7 per group.