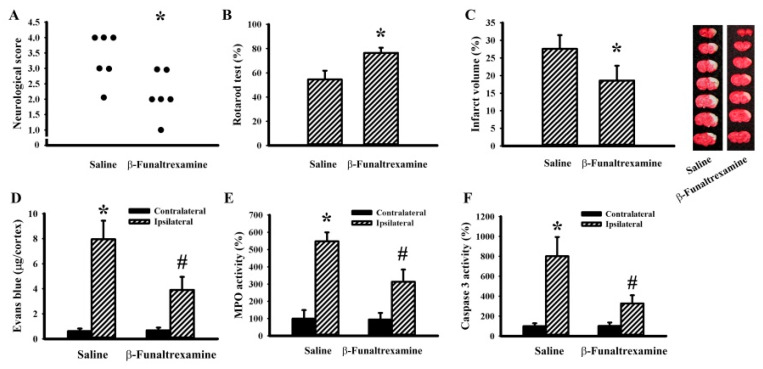
Figure 6.
β-funaltrexamine protected against cerebral I/R injury. Rats receiving normal saline vehicle or β-funaltrexamine (82.5 nmol/30 μL) intracerebroventricular infusion were subjected to both Common Carotid Arteries (CCAs) and the right middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion for 90 min followed by 24-h reperfusion. (A) Neurological deficits were evaluated by neurological score. (B) The motor performance was assessed by a Rotarod test. (C) Representative photographs show the histological examination of a brain infarction by Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride (TTC) staining. The average percentage of infarction volume in the ipsilateral hemisphere is depicted. (D) The contents of Evans blue in contralateral and ipsilateral cortical tissues were measured by an Evans blue extravasation assay. Proteins were extracted from the contralateral and ipsilateral cortical tissues and subjected to an enzymatic assay of Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity (E) and caspase 3 activity (F). * p < 0.05 vs. saline or the contralateral tissues of the vehicle groups and # p < 0.05 vs. the ipsilateral tissues of the vehicle groups, n = 6.