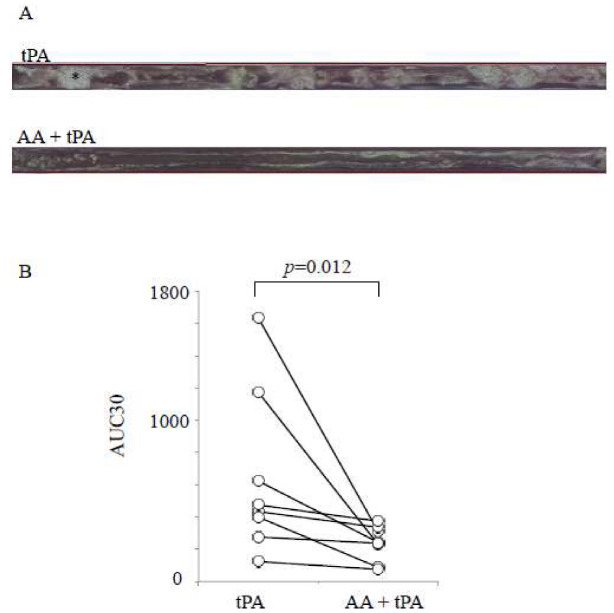
Figure 6.
Effect of l-ascorbic acid on recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator-induced fibrinolysis under flow conditions in human whole blood. (A) Representative video microscopy images of fibrinolysis over 18–19 min in samples exposed to recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rtPA) or AA–tPA in human whole blood. The asterisk shows an example of thrombi (white area). (B) Area under the curve at 30 min (AUC30) following tPA treatment and AA and tPA treatment in human whole blood (n = 8). Overall, the AUC30 was significantly lower following the AA and tPA treatment than the treatment of tPA alone. Values are mean ± SE. Comparisons between two groups were performed using Wilcoxon’s signed rank test.