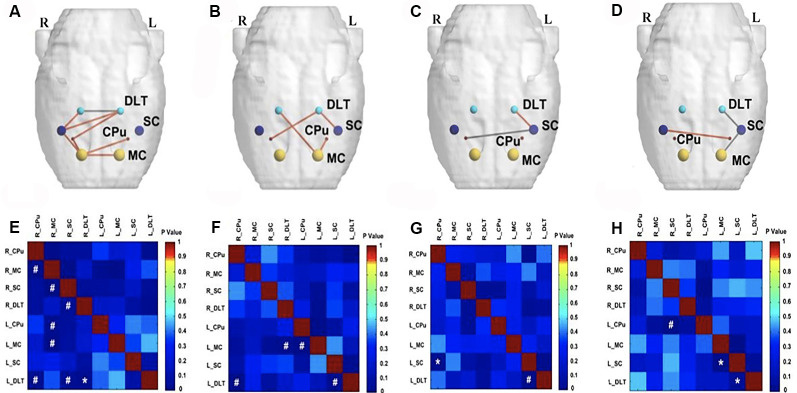
Figure 6.
Comparison of metabolic connectivity among four groups at 16th week (i.e., 4 weeks after EA/sham EA intervention) after BPAI. (A,E) Significantly increased metabolic connectivity among the bilateral motor cortex, bilateral caudate putamen, bilateral DLT, and right somatosensory cortex, as well as significantly decreased metabolic connectivity between bilateral DLT were observed in the EA group compared with the sham EA group. (B,F) Significantly increased metabolic connectivity was observed among the bilateral DLT, left motor cortex, left somatosensory cortex, and right caudate putamen in the EA group compared with the model. (C,G) Significantly increased metabolic connectivity between the left DLT and left somatosensory cortex, as well as decreased metabolic connectivity between left somatosensory cortex and right caudate putamen were observed in the sham EA group compared with the model group. (D,H) Changes of metabolic connectivity in the whole brain after BPAI (*P < 0.05; #P < 0.001). Red line, increased metabolic connectivity; gray line, decreased metabolic connectivity. BPAI, brachial plexus avulsion injury; EA, electroacupuncture; SC, somatosensory cortex; DLT, dorsolateral thalamus; MC, motor cortex; CPu, caudate putamen.