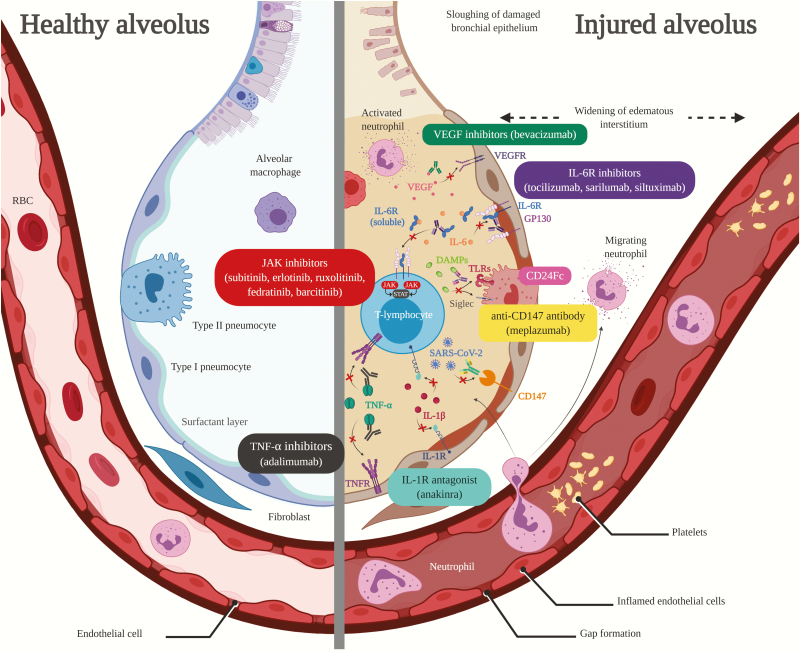
Figure 1.
Figure compares healthy alveolus (left) to injured alveolus (right) from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-induced proinflammatory host response and proposed targets of immunomodulatory therapy in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-related acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor (VEGF) inhibitors (green text box) bind to and neutralize VEGF to inhibit pulmonary edema caused by VEGF overexpression. Interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) inhibitors (purple text box) inhibit both membrane-bound IL-6R and soluble IL-6R leading to inhibition of IL-6R activation and hyper-IL-6 formation, whereas siltuximab also binds directly to IL-6. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors (red text box) inhibit the activity JAK enzymes thereby interfering with the JAK/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway responsible for inflammatory cytokine signaling. CD24Fc (pink text box) interacts with danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectins (Siglecs) to inhibit nuclear factor-kappa B activation and release of inflammatory cytokines. Anti-CD147 antibodies (yellow text box) inhibit CD147, which may lead to decreased SARS-CoV-2 replication. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α inhibitors (black text box) bind to TNF-α to prevent binding to TNF-α receptor (TNFR) sites and subsequent release of inflammatory cytokines. Interleukin-1R antagonists (blue text box) block activity of IL-1β by competitively inhibiting binding to IL-1R. RBC, red blood cell; TLR, Toll-like receptor. Created with BioRender.com.