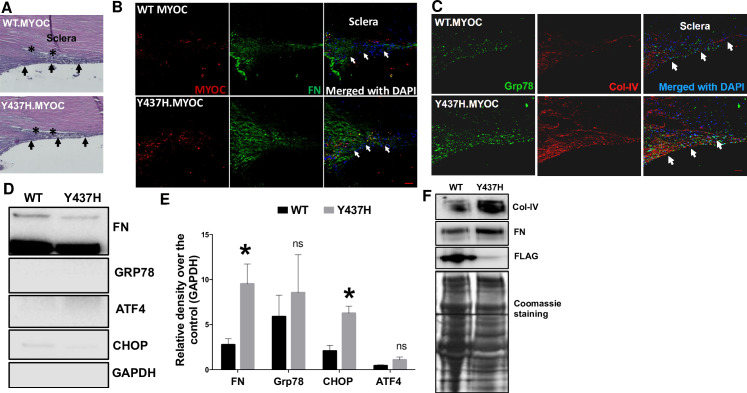
Fig 6. Lentiviral expression of mutant myocilin induces ER stress and ECM changes in the TM of cultured corneoscleral segments.
The cultured corneoscleral quadrants were transduced with FTS tagged (FLAG & S tag) WT myocilin or mutant myocilin (Y437H) expressing lentiviral particles (1ml of lentivirus supernatant) for 7 days. A) H&E staining and (B&C) immunostaining for myocilin, FN, GRP78 and Col-IV in cultured corneoscleral segments transduced with WT or mutant myocilin. Increased myocilin staining was observed in the TM of mutant myocilin-transduced quadrants compared to WT myocilin. In addition, increased FN and Col-IV staining indicate more ECM accumulation in the TM of mutant myocilin-transduced quadrants (n = 3 biological replicates, scale bar is 50μm). Western blot and densitometric analysis of TM tissue lysates (D-E) and conditioned medium (F) obtained from cultured quadrants transduced with WT and mutant myocilin lentiviral expression vectors. A significant increase in the ECM marker FN (n = 6 biological replicates) and the ER stress marker CHOP (n = 3 biological replicates) was observed in mutant myocilin-transduced TM tissue lysates. Similarly, conditioned medium (F) from mutant myocilin-treated corneoscleral segments showed increases in ECM proteins FN and Col IV. Moreover, WT myocilin was detected in conditioned media of WT myocilin-transduced quadrants while no myocilin was detected in quadrants expressing mutant myocilin indicating that expression of mutant myocilin inhibits its secretion and accumulates in the TM cells. Unpaired t-test, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Arrows indicate the TM region.