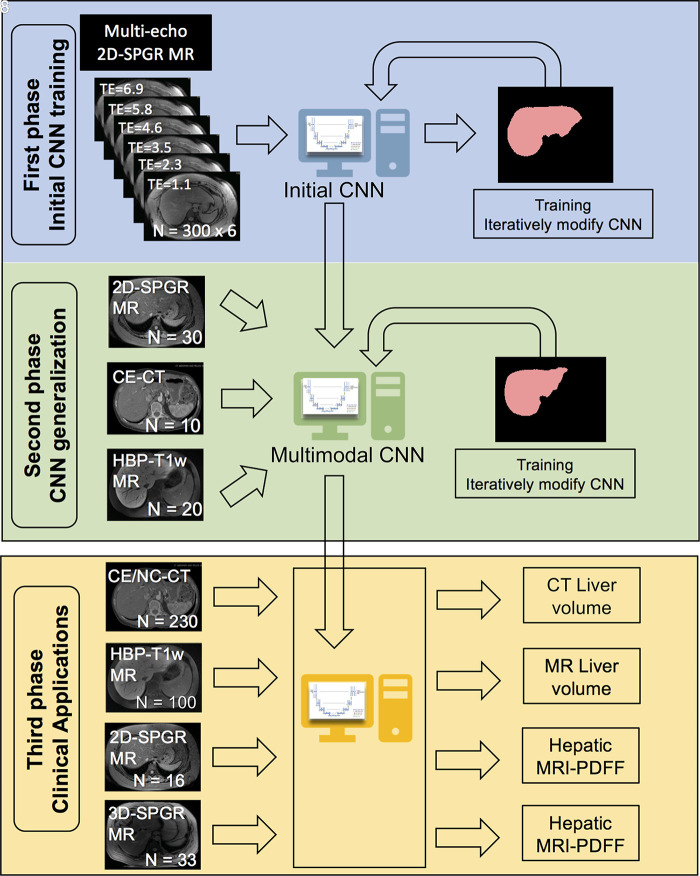
Figure 1:
Overview of the study design, which comprised three phases. In the first phase, we trained with unenhanced low-flip-angle two-dimensional (2D) multiecho spoiled gradient-echo (SPGR) MR images with variable T2* weighting (n = 300) with multiple echo times (TEs) to be robust against different signal weightings. In the second phase, we used transfer learning to generalize our convolutional neural network (CNN) to other imaging modalities by using multimodal image data (30 2D SPGR MRI datasets, 10 contrast-enhanced CT datasets, 20 contrast-enhanced T1-weighted hepatobiliary phase MRI datasets). In the third phase, we assessed the accuracy of liver segmentation, liver volumetry, and hepatic proton density fat fraction (PDFF) estimation. 3D-SPGR = unenhanced low-flip-angle three-dimensional multiecho spoiled gradient-echo MRI with variable T2* weighting; CE/NC-CT = contrast-enhanced and unenhanced CT; HBP-T1w MR = contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI in the hepatobiliary phase performed about 20 minutes after injection of 0.025 mmol per kilogram of body weight gadoxetate disodium, a hepatobiliary agent.