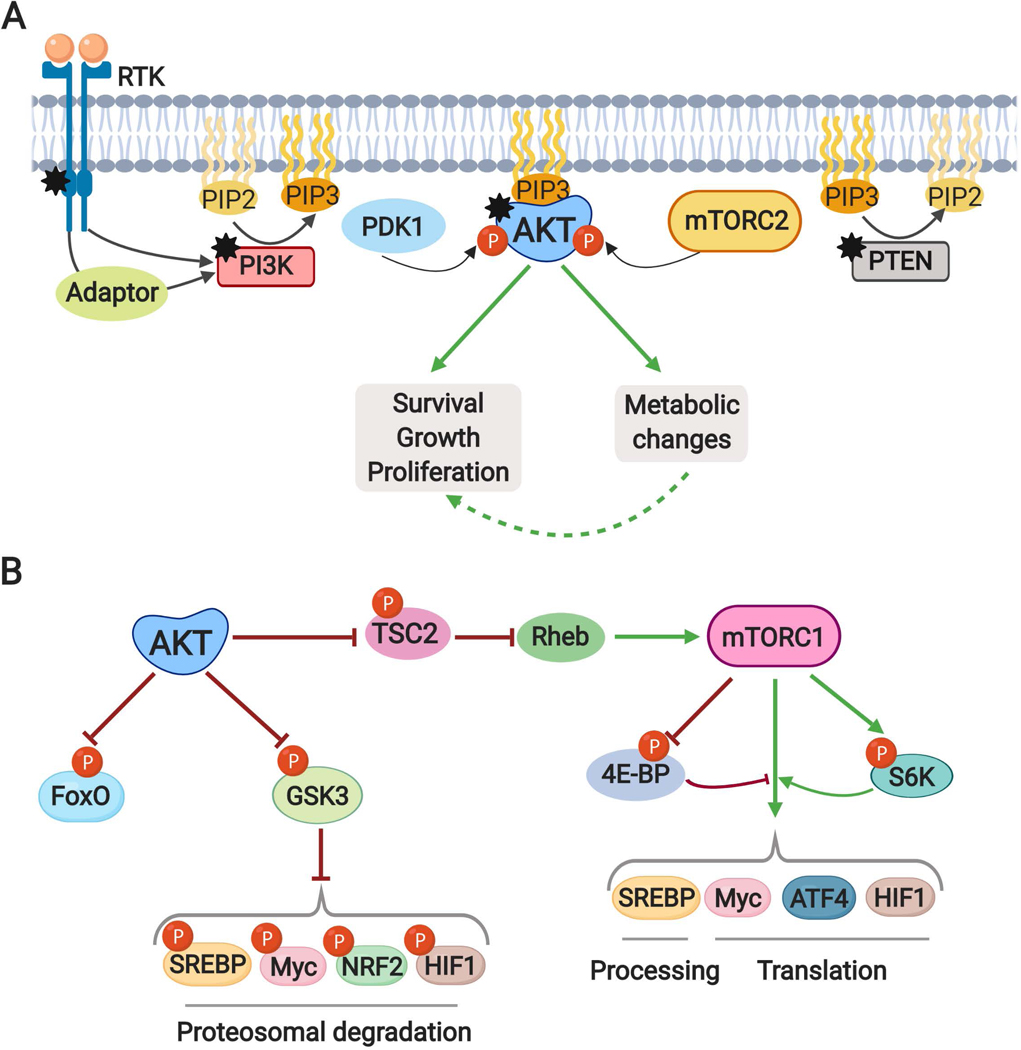
Fig. 1: The PI3K-AKT pathway and its major downstream effectors.
A. Mechanisms of AKT activation. Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) activation and tyrosine phosphorylation of its cytosolic domain or of scaffolding adaptors create binding sites that recruit the lipid kinase PI3K to the plasma membrane. PI3K phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to produce phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3), which can be dephosphorylated back to PIP2 by the lipid phosphatase PTEN. PIP3 acts as a second messenger to recruit the serine/threonine protein kinase AKT to the plasma membrane, where it is fully activated through phosphorylation at T308 and S473 by the PDK1 and mTORC2 protein kinases, respectively. AKT signaling serves to promote cell survival, growth, and proliferation, in part, by inducing various changes to cellular metabolism. Coloured hexagons denote common points of activation and inactivation by cancer-associated mutations. “P” indicates protein phosphorylation events.
B. AKT controls cellular metabolism, in part, through three key downstream substrates: TSC2, GSK3, and the FOXO transcription factors. AKT phosphorylates and inhibits TSC2, a component of the TSC complex, to activate mTORC1 by relieving TSC complex-mediated inhibition of Rheb. S6K1 and 4EBP1 are canonical downstream targets of mTORC1, which together with other targets, serve to stimulate the processing and activation of the SREBP family of transcription factors and the mRNA translation of the MYC, HIF1α, and ATF4 transcription factors. GSK3-mediated phosphorylation of the transcription factors SREBP, MYC, NRF2, and HIF1α targets them for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation.
PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; PDK1, phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1; mTORC2, mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex 2; mTORC1, mTOR complex 1; TSC2; tuberous sclerosis complex 2; GSK3, Glycogen synthase kinase 3; FOXO, forkhead box O; Rheb, Ras homolog enriched in brain; S6K1, Ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1; 4EBP1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein, SREBP: Sterol regulatory element binding proteins; HIF1, Hypoxia-inducible factor 1, ATF4, activating transcription factor 4, NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2.