Fig. 6. Dopaplex gene expression program increases bursting activity of MSNs and enhances cocaine locomotor sensitization.
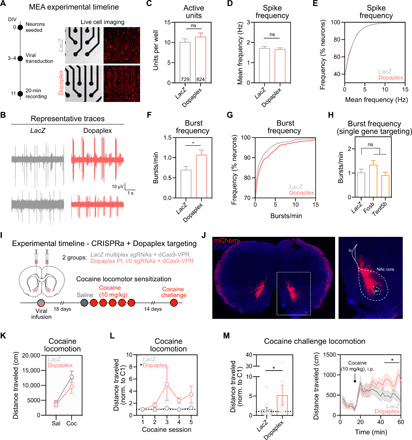
(A) Left: Experimental timeline for viral transduction and MEA recordings. Right: Live cell imaging demonstrating CRISPRa lentivirus expression. (B) Representative single-unit voltage traces. The number of active units per well (C) and action potential frequency (D and E) did not change following Dopaplex targeting (P > 0.275 for both comparisons). (F) Burst frequency is increased in Dopaplex-targeted neurons (n = 729 to 824 neurons per group, *P = 0.0265). (G) Cumulative distribution of burst frequency. (H) Burst frequency was not altered when CRISPRa was targeted to single genes within the Dopaplex gene expression program (n = 356 to 372 neurons per group, P = 0.1012). (I) Experimental timeline for viral transduction and cocaine locomotor sensitization. (J) Representative image of sgRNA viral transduction (mCherry reporter) in the NAc. (K) Absence of baseline locomotion difference between LacZ and Dopaplex-targeted animals following the first cocaine injection (n = 12 to 14 rats per group, P = 0.3474). (L) Over five cocaine administration sessions, Dopaplex-targeted animals exhibited increased locomotion (*P = 0.0464). (M) Cocaine challenge injection revealed enhanced locomotor sensitization in Dopaplex-targeted rats (*P = 0.0270). All data are expressed as means ± SEM.
