(
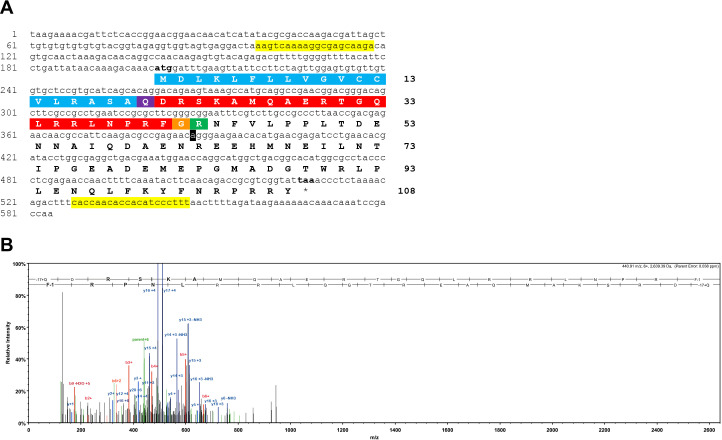
A) Sequence of a cDNA encoding the precursor of a NPY/NPF/PrRP-like peptide in
A. rubens. The cDNA sequence (lowercase) comprises an open reading frame of 324 bases that encode a 108-residue protein (uppercase). The predicted signal peptide is shown in blue, the predicted cleavage site is shown in green and the predicted neuropeptide is shown in red, with an N-terminal glutamine that is a potential substrate for pyroglutamation shown in purple and with a C-terminal glycine that is a potential substrate for amidation shown in orange. The cDNA was amplified by PCR from
A. rubens radial nerve cord cDNA using primers corresponding to the sequences highlighted in yellow. The cDNA was cloned in the vector pBluescript II SK (+) and the T3 and T7 primers were used for the sequencing. A single nucleotide that differs from a contig sequence (1060225) identified from
A. rubens radial nerve cord transcriptome data is highlighted in black, but this is a synonymous substitution. This sequence has been deposited in GenBank under the accession number
MK033631.1 (
B) Annotated mass spectrum showing the structure of a NPY/NPF/PrRP-like peptide isolated from an
A. rubens radial nerve cord extract. The peptide QDRSKAMQAERTGQLRRLNPRF, with Q1-Pyroglutamate (−17.02655 Da) and F22-amidated (−0.98402 Da), was observed at charge state +6, monoisotopic m/z 440.90631 Da with a precursor mass error of 0.12 ppm [MH+ 2640.40148 Da] and with a retention time (RT) of 66.3484 min. The b series of peptide fragment ions are shown in red, the y series in blue and additional identified peptide fragment ions in green. The peptide was identified with: Sequest HT (v1.17); XCorr: 4.27, Percolator q-Value: 0.0e0, Percolator PEP:1.6e-2. The fragment match tolerance used for the search was 0.8 Da. The fragmentation table for this mass spectrum can be found in
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1.