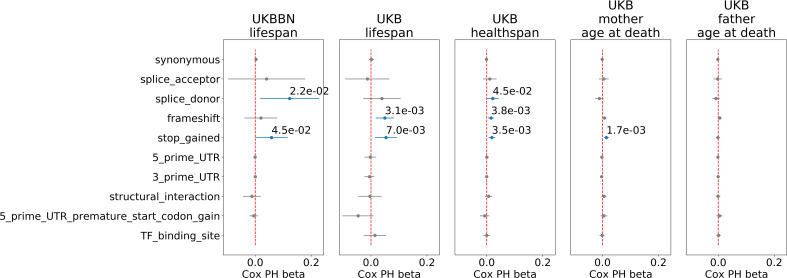
Figure 3. Association of ultra-rare () variants burden with UKB and UKBBN lifespan, UKB healthspan, and parental longevity (father’s and mother’s age at death).
The number of ultra-rare variants belonging to each category was calculated for each genome and tested for association with lifespan phenotypes using Cox proportional hazards model and covariates to account for population structure. UKBBN lifespan was tested using sex and 20 first principal components (PCs) taken from principal component analysis of common variants shared between UKBBN and 1000G project. UKB lifespan during follow-up was tested for association with ultra-rare variants burdens using sex, age of enrollment, assessment centers, and 40 PCs provided by UKB as covariates. Sex, assessment centers, and 40 PCs were used as covariates for associations with UKB healthspan, and mother’s and father’s age at death. Beta coefficients estimated by Cox proportional hazards model (Cox PH beta) are plotted as dots with whiskers representing 95% confidence intervals. p-Values are shown for significant results only. Blue color designates statistically significant associations. Red dashed line designates zero Cox PH beta coefficient value. UKB - UK Biobank, UKBBN - UK Brain Bank Network, TF - transcription factor, UTR - untranslated region, MAF - minor allele frequency, PTV - protein-truncating variants (defined as stop codon gains, frameshifts, canonical splice acceptor/donor sites).