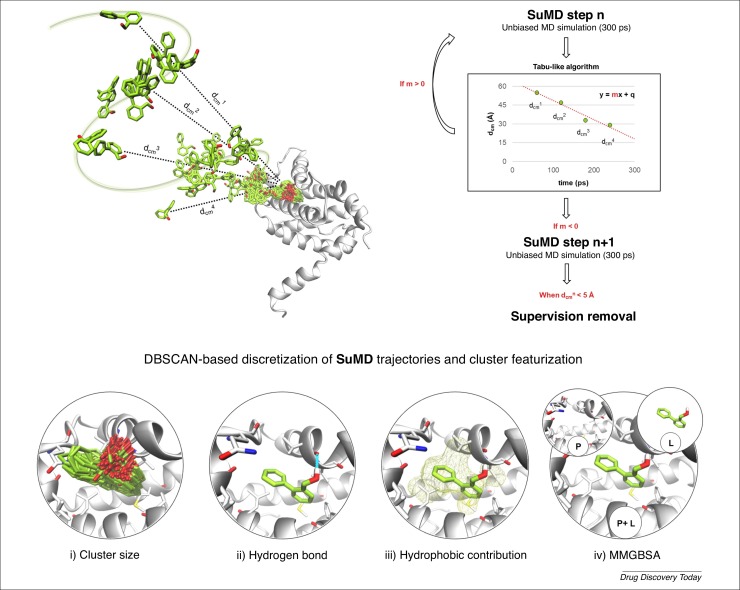
Figure 1.
High-throughput supervised molecular dynamics (HT-SuMD), an automated protocol exploiting molecular simulation to perform fragment screening. The SuMD methodology is summarized with a specific focus on the tabu-like algorithm controlling acceptance or rejection of short unbiased MD simulations, depending on how the distance between the fragment under investigation and the binding site center of mass (dcmn) changes during the trajectory. A density-based clustering algorithm (DBSCAN) clustering algorithm is used to perform a geometrical discretization of SuMD trajectories and identify relevant fragment conformations. Each cluster is then characterized based on four geometric and energetic indicators: (i) cluster size; (ii) hydrogen bond presence; (iii) hydrophobic contribution of binding; and (iv) protein–ligand MMGBSA binding interaction energy. Once all clusters have been characterized, a consensus scoring filter is applied to identify hit fragment molecules.