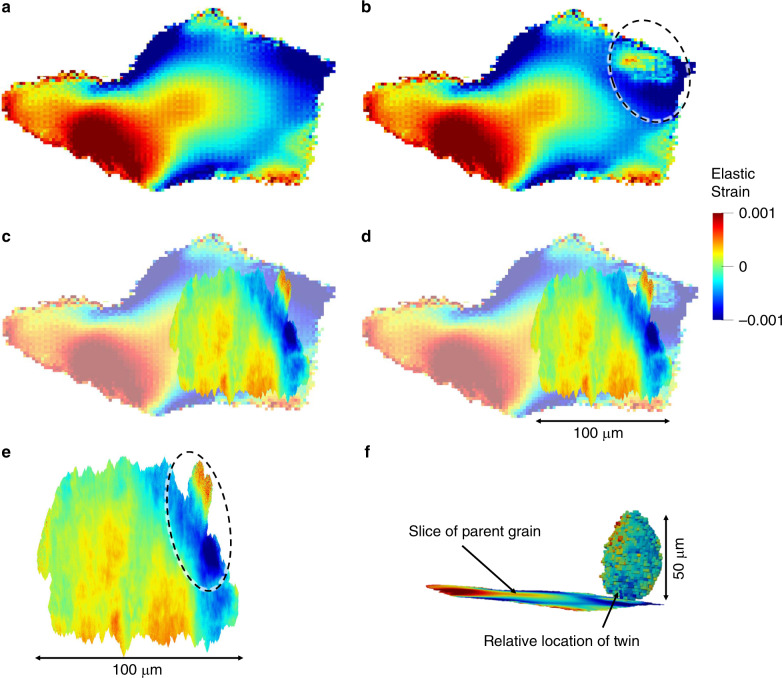
Fig. 5. DFXM and CP-FFT Comparison – Elastic Strain.
(a) CP-FFT model result of elastic strain without twin instantiation; (b) with twin instantiation. (c) CP-FFT model from a with DFXM overlay from e. (d) CP-FFT model from b with DFXM overlay from e. (e) Elastic strain from DFXM combined mosaicity and elastic strain scan. (f) Relative position of twin boundary to the 2D slices a–e. All strains are of the elastic strain component normal to the (220) planes of interest.