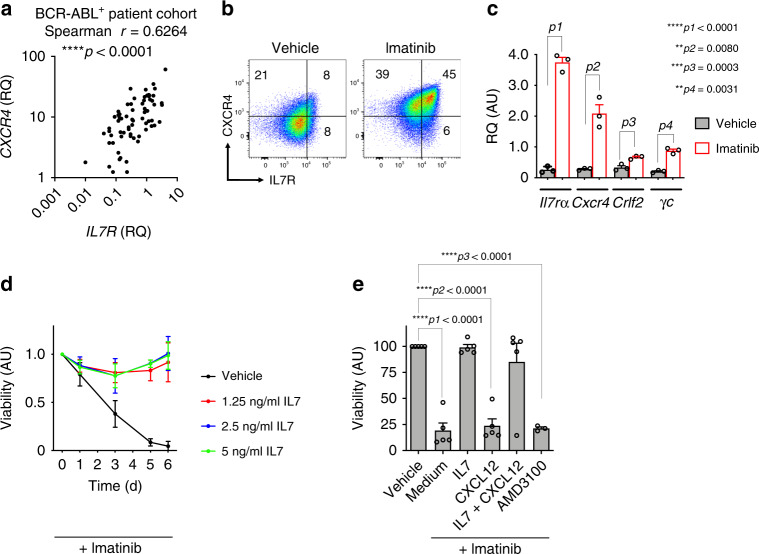
Fig. 2. Regulation of IL7R and CXCR4 expression levels in BCR-ABL+ ALL.
a Correlation analysis between IL7R and CXCR4 expression levels in 68 pediatric BCR-ABL+ ALL patients. Two-tailed Spearman correlation analysis; exact p value = 0.000000011054191. b Flow cytometry analysis showing that imatinib treatment (1 µM; 15 h) leads to increased expression of IL7R and CXCR4 on the cell surface of BCR-ABL1-transformed cells. The results are representative of three independent experiments. c Quantitative RT-PCR showing that Il7r and Cxcr4 and other associated factors are regulated at the level of transcription. N = 3 independent samples per group, and error bars represent mean ± SEM. Unpaired t-test, two-sided, p1 exact value = 0.000035569652955. RQ: relative quantification; AU arbitrary unit. d BCR-ABL1-transformed WT pre-B cells were treated with 1 µM imatinib and with different concentrations of IL7 as indicated for 6 days. N = 3 independent samples per group, and error bars represent mean ± SD. One-way ANAOVA. Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test was performed to day 6, compared with control group (Vehicle). Adjusted p values: Vehicle vs. 1.25 ng/ml IL7 ***p = 0.0003, Vehicle vs. 2.5 ng/ml IL7 ***p = 0.0002, Vehicle vs. 5 ng/ml IL7 ***p = 0.0002. e Treatment of BCR-ABL1-transformed cells with imatinib leads to cell death and concomitant incubation with IL7, but not CXCL12, reverses this effect. N = 3 independent samples per group, and error bars represent mean ± SEM. Unpaired t-test, two-sided, ****p1 exact value = 0.000003416387742, ****p2 exact value = 0.000002948485097, ****p3 exact value = 0.000000000342967.