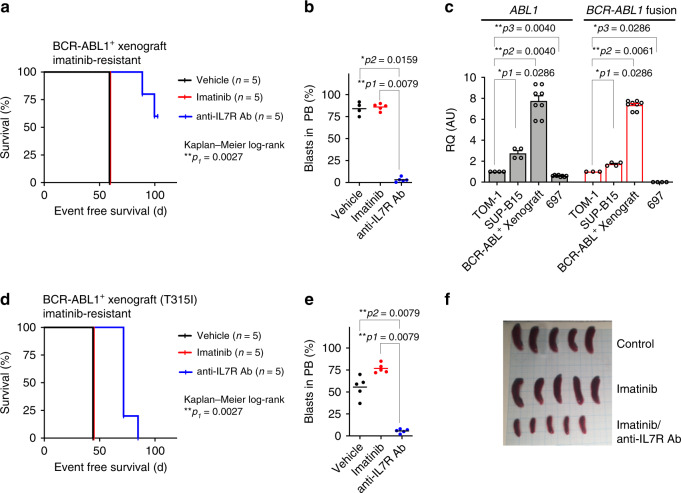
Fig. 7. Anti-IL7R antibody suppresses BCR-ABL1+ ALL development in vivo.
a, b 1 × 106 BCR-ABL1+ ALL patient cells were xenografted by tail vein injection into NSG mice. Xenografted mice were treated with vehicle, imatinib, or with anti-IL7R antibody (n = 5 per group) as described in “Methods”. a Survival prolongation in xenografted mice subjected to the indicated treatment. Mantel–Cox-log-rank test, **p = 0.0027. b Leukemic engraftment was measured by flow cytometry in peripheral blood (PB) at day 58 and all control and imatinib-treated mice were sacrificed due to appearance of leukemic symptoms. Unpaired t-test, two-sided p value. c Expression levels of ABL1 or BCR-ABL1 fusion in BCR-ABL1+ human cell lines (TOM-1 and SUP-15), and in imatinib-resistant xenograft-derived human BCR-ABL1+ cells. 697 cell line, was used as a negative control for the fusion. Expression levels are normalized to TOM-1. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. Unpaired t-test, two-sided. RQ: relative quantification; AU arbitrary unit. d–f 1 × 106 BCR-ABL1+ ALL patient cells holding T315I mutation (imatinib-resistant) were injected intravenously into NSG mice and treated with anti-IL7R antibody or with imatinib. d Survival prolongation in mice xenografted with Ph+ BCP-ALL patient material holding the T315I mutation and treated with either imatinib or with anti-IL7R antibody. Mantel–Cox-log-rank test, **p = 0.0027. e Leukemic engraftment was measured by flow cytometry in PB at day 42. Unpaired t-test, two-sided. f Spleen size at day 45 of xenograft mice treated with either imatinib or a combination of imatinib and anti-IL7R antibody.