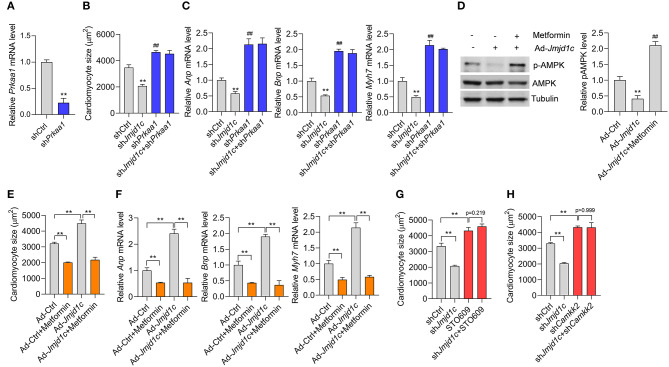
Figure 6.
AMPK participates in the role of JMJD1C during cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. (A) Prkaa1 knockdown in cardiomyocytes. The cells were treated with adenovirus expressing shPrkaa1 or with a control virus for 48 h (B,C). Prkaa1 knockdown blocks the influence of Jmjd1c knockdown on Ang II-induced increase in cardiomyocytes. The cells with/without Prkaa1 or Jmjd1c knockdown were subjected to hypertrophy induction with Ang II for 48 h. Then cardiomyocyte size (B) and gene expression (C) were analyzed. **p < 0.01 vs. shCtrl. ##p < 0.01 vs. shCtrl (D). Metformin activates AMPK. The indicated cardiomyocytes were treated with metformin (1 mM) for 24 h. **p < 0.01 vs. Ad-Ctrl; ##p < 0.01 vs. Ad-Jmjd1c. n = 3 in each group (E,F). Metformin-mediated activation of AMPK blocks the influence of JMJD1C overexpression on cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by Ang II stimuli. NRCMs were infected with/without adenovirus carrying Jmjd1c for 24 h; then the cells were treated with Ang II (1 μM) metformin (1 mM) for an additional 48 h. Cardiomyocyte size (E) and gene expression (F) were analyzed **p < 0.01. (G) STO-609 blocks the influence of Jmjd1c knockdown on the Ang II-induced increase in cardiomyocytes. **p < 0.01. (H) Camkk2 knockdown blocks the influence of Jmjd1c knockdown on Ang II-induced increase in cardiomyocytes. **p < 0.01. All results are from three independent experiments.