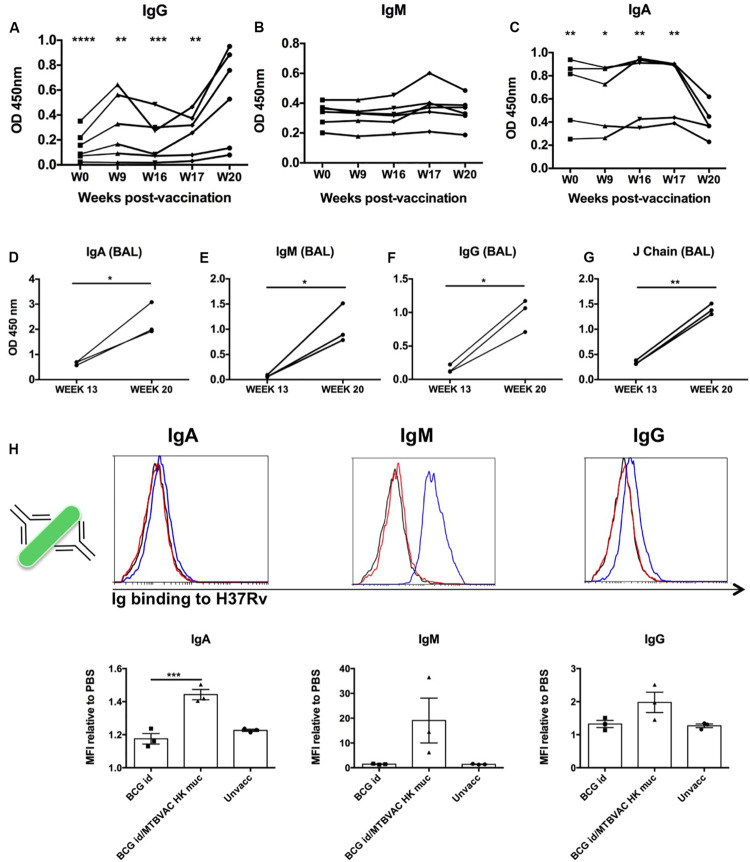
FIGURE 5.
Intrabronchial MTBVAC HK induces mucosal immunoglobulins in respiratory airways from non-human primates. (A–C) PPD-specific IgG, IgM, and IgA were measured in sera samples from the different individuals throughout the vaccination phase (until week 20). (D–G) PPD- specific IgA, IgM, IgG, as well as J chain were analyzed in BAL samples harvested at week 13 (before MTBVAC HK) and week 20 (after MTBAVC HK) from three individuals from the MTBVAC HK group. Data in the graphs show values for each individual (H) Direct binding of IgA, IgM, and IgG to Mtb surface. H37Rv bacteria were incubated with BAL samples and immunoglobulin binding measured by flow cytometry using specific secondary antibodies. Representative overlay histograms are shown. Black line: unvaccinated; Red line: BCG vaccinated; Blue line: BCG/MTBVAC HK vaccinated. Data in the graphs show the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) obtained with each BAL compared to the measured when bacteria are incubated with PBS. (A–G) Data show individual from one experiment. (F) Data are shown as mean ± SEM and are representative of two independent experiments. (A–C, H) *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-test. (A–C) Comparisons of the different timepoints with week 20 are shown. (D–G) *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 by paired t-student test.