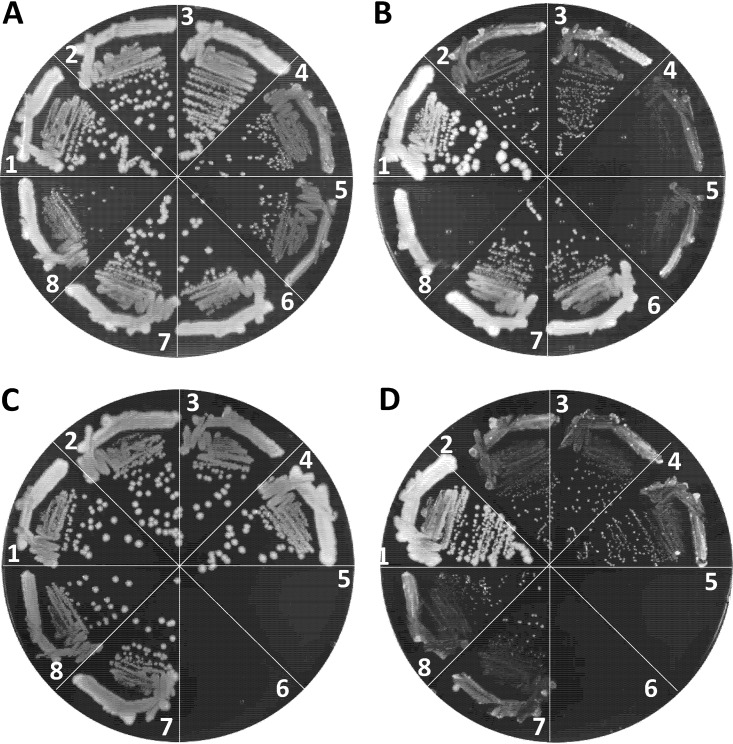
FIG 7.
Effects of ompR and porin gene mutations on the growth of ΔtonB or ΔtonB ΔaroB mutants. Bacterial growth was monitored on LBA plus 40 μM FeCl3 (A and C) and LBA (B and D) after incubation of petri plates at 37°C for 24 h. Relevant genotypes of strains used in panels A and B: 1, RAM1292 (wild type); 2, RAM2572 (ΔtonB); 3, RAM2765 (ΔtonB malPQ::Tn10); 4, RAM2766 (ΔtonB malPQ::Tn10 ompR101); 5, RAM2767 (ΔtonB ΔompR::Kmr); 6, RAM2574 (ΔtonB ΔaroB::Kmr); 7, RAM2771 (ΔtonB ΔaroB::Kmr malPQ::Tn10); and 8, RAM2772 (ΔtonB ΔaroB::Kmr malPQ::Tn10 ompR101). Relevant genotypes of strains used in panels C and D: 1, RAM1292 (wild type); 2, RAM2572 (ΔtonB); 3, RAM2769 (ΔtonB ΔompC::Cmr); 4, RAM2768 (ΔtonB ΔompF::Kmr); 5 and 6, no bacteria; 7, RAM2792 (ΔtonB ΔompC::Cmr ΔompF::Kmr/pompC); and 8, RAM2790 (ΔtonB ΔompF::Kmr ΔompC::Cmr/pompF). pompF and pompC are pTrc99A plasmid clones expressing ompF and ompC, respectively. The expression of these plasmid-coded genes did not require induction by an inducer.