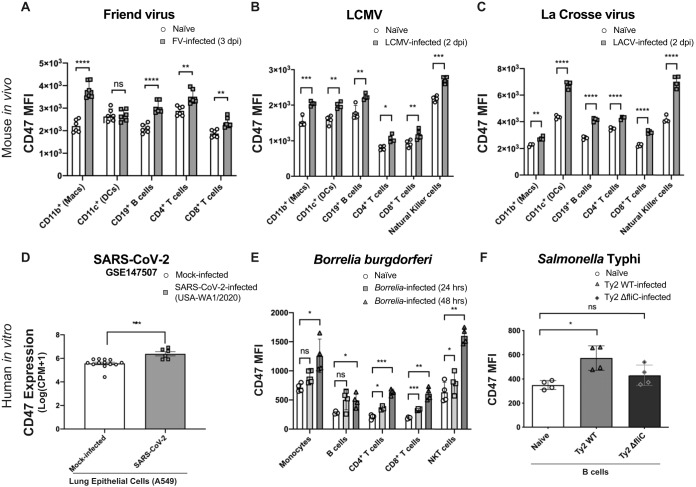
FIG 1.
CD47 is broadly upregulated in immune cell types in response to several types of infection. (A and B) Comparison of CD47 median fluorescence intensities (MFI) on splenic hematopoietic cell subsets from naive mice and female (A.BY × C57BL/6)F1 mice infected intravenously with 2 × 104 SFFU Friend virus at 3 days postinfection (A) or female C57BL/6 mice infected intravenously with 2 × 106 PFU LCMV-WE at 2 days postinfection (B). (C) Female C57BL/6 mice inoculated intraperitoneally with 105 PFU La Crosse virus at 2 days postinfection. (D) CD47 expression levels analyzed from the publicly available gene expression data set from SARS-CoV-2 infection of A549 human lung tumor cells (GEO accession number GSE147507) (n = 10) comparing mock-infected (n = 13) with SARS-CoV-2 (USA-WA1/2020)-infected cells (n = 6). (E) Comparison of CD47 MFI on hematopoietic cells from Borrelia burgdorferi-GFP-infected human PBMCs 24 and 48 h after in vitro infection, compared to naive controls. GFP was used under infection conditions to identify cells with intracellular Borrelia infection (shaded). (F) Comparison of CD47 MFI on human CD19+ B cells 24 h after in vitro infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi strain Ty2 (Ty2 WT) or Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi strain ΔfliC (Ty2 ΔfliC), which lacks flagella, compared to naive controls. Statistical analyses were done by Student’s t tests for panels A to D and by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a multiple-comparison posttest for panels E and F (ns [not significant], P > 0.05; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001). Error bars represent standard errors of the means (SEM).