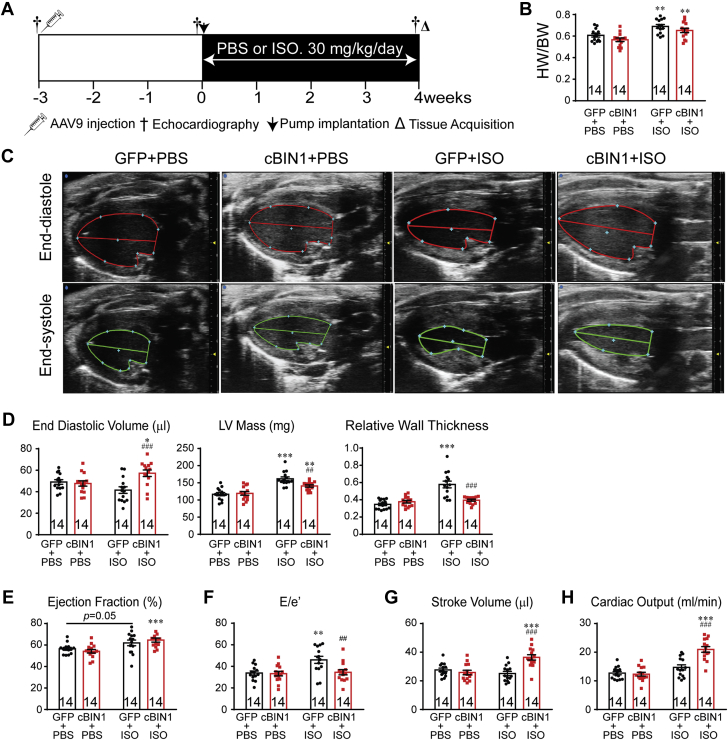
Figure 1.
Exogenous cBIN1 Reduces Concentric Hypertrophy in Post-ISO Mouse Hearts
(A) Experimental protocol: 56 mice were randomized into 4 experimental groups: AAV9-GFP+PBS, AAV9-GFP+ISO, AAV9-cBIN1+PBS, and AAV9-cBIN1+ISO (n = 14/group). (B) Mouse HW/BW in the 4 groups. (C) Representative images of longitudinal axis view of left ventricles at both end diastolic and end systolic phase at 4 weeks post-PBS or ISO infusion. Echocardiography analysis of end diastolic volume, LV mass, and relative wall thickness (D), ejection fraction (E), E/e’ (F), stroke volume (G), and cardiac output (H) is also included. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA was used followed by Fisher LSD test for multiple comparison. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001, for PBS vs. ISO comparison within each AAV9 treatment group ##p <0.01 and ###p <0.001 for GFP vs. cBIN1 comparison within each drug infusion group. AAV9 = adeno-associated virus 9; ANOVA = analysis of variance; BW = body weight; cBIN1 = cardiac bridging integrator 1; GFP = green fluorescent protein; HW = heart weight; ISO = isoproterenol; LSD = least significant difference; LV = left ventricular; PBS = phosphate-buffered saline; SEM = standard error of the mean.