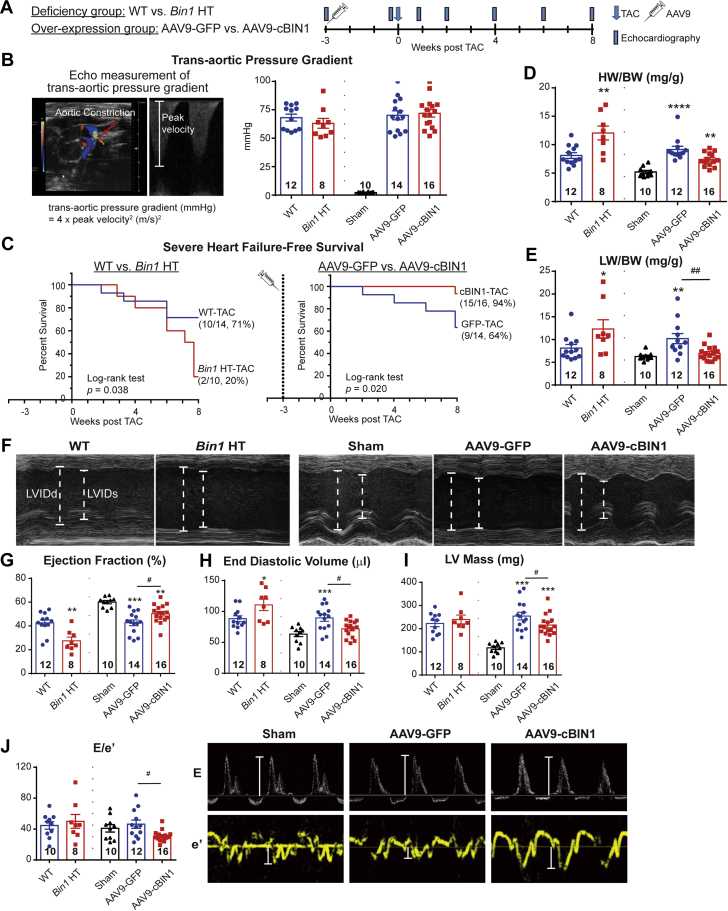
Figure 8.
cBIN1 Gene Transfer Improves Heart Failure–Free Survival in Post-TAC Mice
(A) Schematic protocol for the TAC study. (B) Trans-aortic pressure gradient measurement in all mice 5 days post-surgery. (C) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for heart failure–free survival (non-survival is death or EF <35%) in WT vs. Bin1 HT mice (left), and AAV9-GFP or cBIN1 pretreated mice (right). Log-rank test was used for survival comparison. HW/BW (D) and LW/BW (E) in all mice at 8 weeks post-TAC. (F) Representative M-mode echocardiography images of all mice 8 weeks after surgery. Echocardiography-measured left ventricular ejection fraction (G), end diastolic volume (H), LV mass (I), and E/e’ (J) for all mice at 8 weeks post-TAC. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Representative E and e’ images in the AAV9 treatment groups are included (right panel of J). Unpaired Student's t-test (or nonparametric Mann-Whitney test used for comparison between WT and Bin1 HT. One-way ANOVA or Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Fisher LSD test for multiple comparison was used for comparison among Sham, AAV9-GFP, and AAV9-cBIN1. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 for comparison vs. WT or Sham; #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 for comparison of AAV9-GFP vs. AAV9-cBIN1. EF = ejection fraction; HT = heterozygote; LW = lung weight; TAC = transverse aortic constriction; WT = wild type; other abbreviations as in Figure 1.