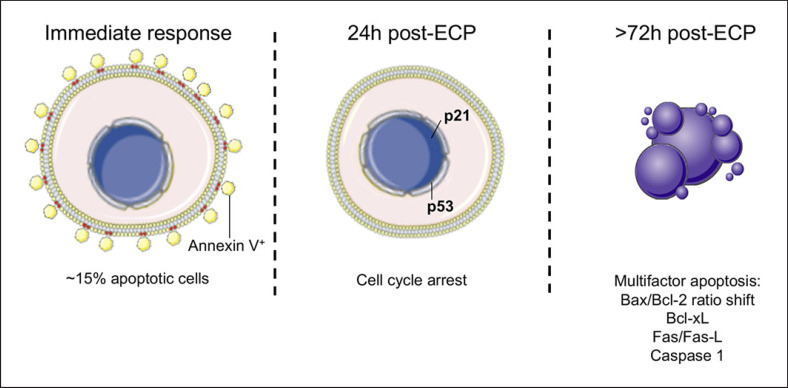
Fig. 1.
Cell cycle arrest and commitment to apoptosis of ECP-exposed cells. Upon exposure to ECP cells that suffer extensive DNA damage, fail to repair it or bear severe mitochondrial alterations initiate a gradual process of apoptosis. Severely affected cells have an immediate flip-flow of phosphatidylserine, others halt cell cycle via activation of p21 and p53, and apoptotic bodies appear as early as 72 h after treatment as a result of activation of both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis pathways.