Figure I.
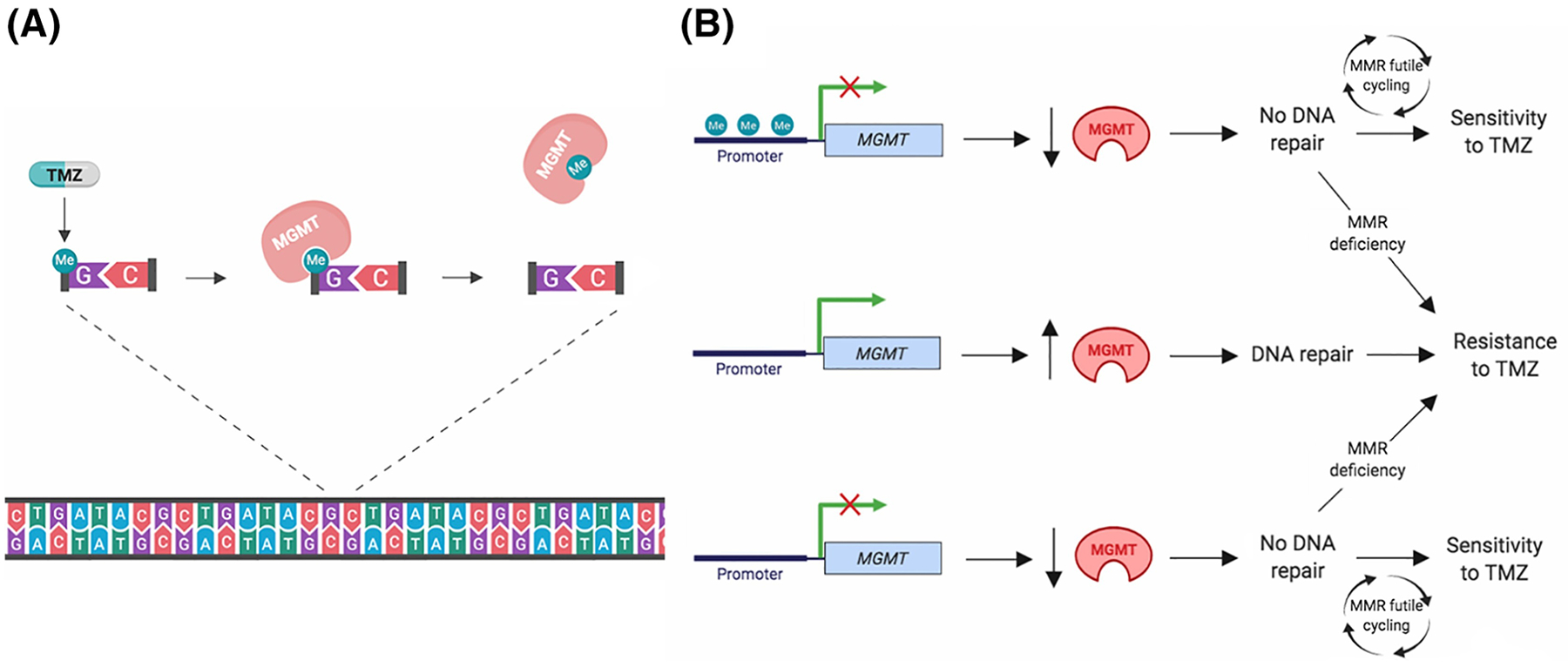
Function of MGMT as determinant of response to TMZ A) Mechanism of MGMT-mediated repair of TMZ-induced DNA damage. Methylation of the O6 position of guanine by TMZ is removed by MGMT, and prevents cell killing by MMR. B) Proposed role of MGMT promoter methylation and expression as determinant of response to TMZ. When the MGMT promoter is methylated (top), silencing of transcription results in low MGMT protein expression. This promotes sensitivity to temozolomide in MMR-proficient cells due to lack of MGMT-mediated DNA damage repair. MMR-deficient cells do not respond to TMZ due to evasion of MMR-dependent DNA double-stranded breaks. When the MGMT promoter is unmethylated (middle), transcription of the MGMT gene results in high expression of MGMT protein, which is able to remove the alkylation adducts, promoting resistance to temozolomide. In some glioblastomas (bottom), MGMT is not expressed in spite of lack of promoter methylation. This promotes sensitivity to TMZ in MMR-proficient cells and resistance in MMR-deficient cells. Created with BioRender.com
