Figure 6.
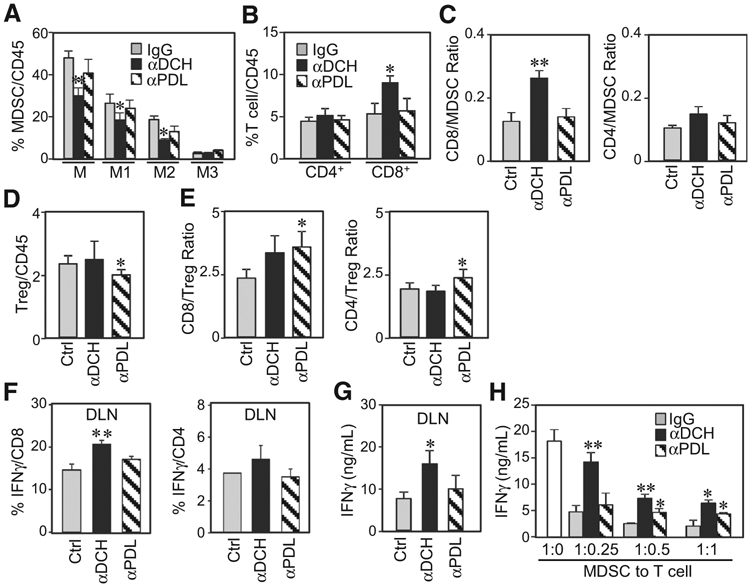
Anti-DC-HIL treatment decreased MDSCs, while increasing CD8 T cells in microenvironments of tumors and draining lymph nodes. CD45+ cells isolated from tumors (A–E) or draining lymph nodes (F and G) of mice treated with control IgG (Ctrl), anti-DC-HIL (αDCH), or anti-PDL1 (αPDL) mAb were determined by flow cytometry for percentage of MDSCs (A), CD4 and CD8 (B), their IFNγ-secreting T cells (F), or Tregs (D). Ratios of CD4 or CD8 T cells to MDSCs (C) or to Tregs (E) were calculated. IFNγ amounts in the DLN were measured (G). H, MDSCs purified from tumors of mice treated with mAb were assayed for their suppressor activity by coculturing with T cells from tumor-free mice in the presence of anti-CD3/CD28 Ab. IFNγ response was determined. *, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.01 compared with Ctrl.
