Fig. 1. 18-mer-HP protects from liver injury after APAP overdose.
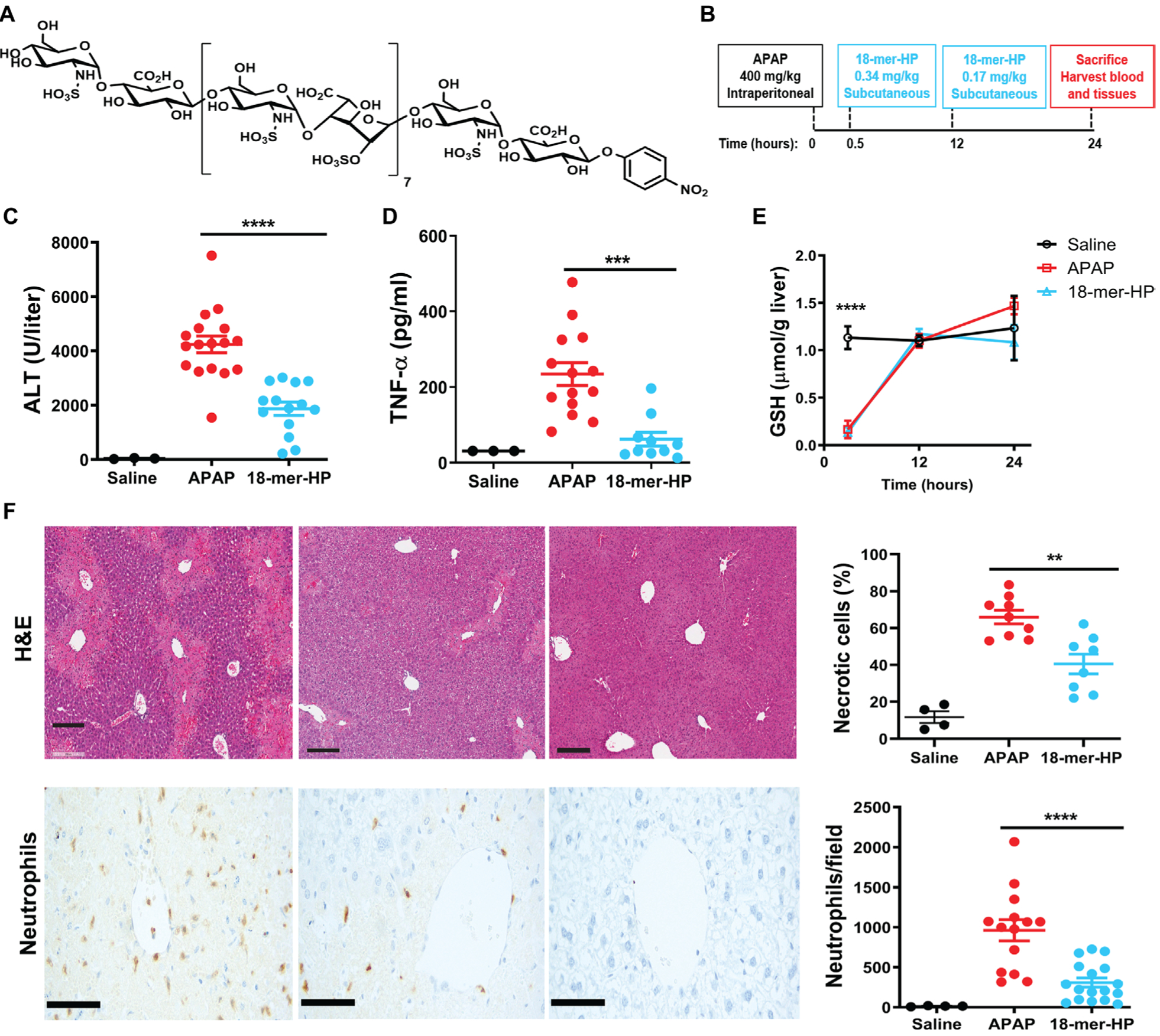
(A) Chemical structure of 18-mer-HP. (B) Murine model experimental design schematic including time, dose, and administration route of APAP and 18-mer-HP. (C) Plasma ALT concentrations from mice treated with saline, APAP alone, and APAP + 18-mer-HP. (D) Plas- ma TNF-α concentrations are decreased in the 18-mer-HP—treated group compared to APAP alone. (E) 18-mer-HP— and APAP-treated mice both have decreased GSH concentrations immediately after APAP overdose compared to the saline control mice. 18-mer-HP does not affect APAP’s metabolism to NAPQI. Saline n= 3, APAP n = 6, 18-mer-HP n = 6. (F) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded liver tissues and neutrophil immunohistochemistry (IHC). Quantitation of H&E-and IHC neutrophil—stained liver tissues from 100× fields are shown on the right. Scale bars, 200 μm. Data represent means ± SEM (C, D, E, and F). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
