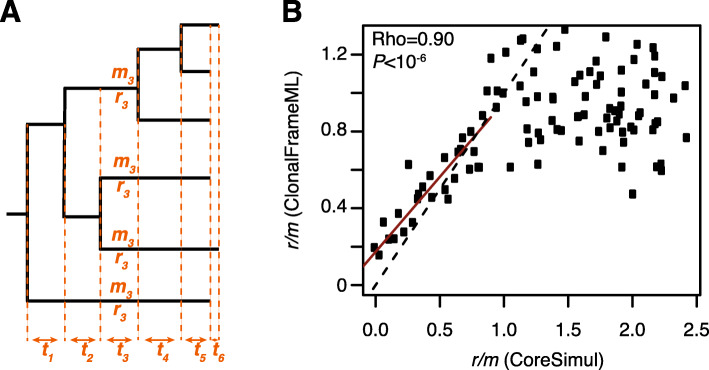
Fig. 1.
a. Schematic representation of the CoreSimul process. The tree is divided in multiple time segments with the same number of overlapping branches. Only branches in the same time segment can recombine with one another. For each branch in the time segment, an average number mt of mutations is introduced following a Poisson distribution and an average number rt of recombination events is introduced—also following a Poisson distribution—between the branches with rt = ρ.mt with ρ the recombination rate. Mutation events and recombination events are introduced in a random order in the different branches of the time segment, simultaneously. b. Comparison between CoreSimul simulations and recombination rate predictions of ClonalFrameML. The black dashed line represents the theoretical expectation between CLonalFrameML predictions and the recombination rates in the simulated dataset. The red line represents the observed linear regression between the simulated r/m values and the r/m values predicted by ClonalFrameML (note that only the data points for r/m ≤ 1 were used for the regression)